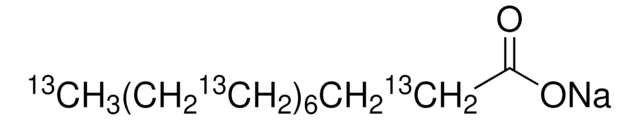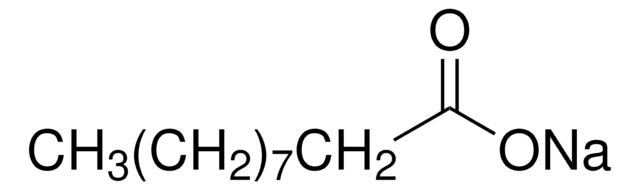P9767
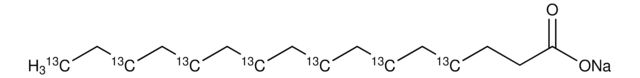
Sodium palmitate
≥98.5%
Sinônimo(s):
Hexadecanoic acid sodium salt, Palmitic acid sodium salt
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
fonte biológica
plant (palm)
Ensaio
≥98.5%
Formulário
powder
pf
283-290 °C (lit.)
grupo funcional
ester
tipo de lipídio
saturated FAs
Condições de expedição
ambient
temperatura de armazenamento
2-8°C
cadeia de caracteres SMILES
[Na+].CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O
InChI
1S/C16H32O2.Na/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16(17)18;/h2-15H2,1H3,(H,17,18);/q;+1/p-1
chave InChI
GGXKEBACDBNFAF-UHFFFAOYSA-M
Procurando produtos similares? Visita Guia de comparação de produtos
Categorias relacionadas
Aplicação
- to induce inflammation and thrombosis pathway in murine macrophage cell line RAW 264.7 cell line by activating reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, Janus-kinase (JNK) signalling and release of histone H3 by western blotting and cell viability by MTT assay
- to induce lipogenesis in AML12 cells and primary hepatocytes to analyse the effect of irisin on PA induced lipogenesis and related signal pathways by western blot analysis and quantitative PCR analysis
- as a component in free fatty acid mixture to induce cellular steatosis in HepG2 cell lines and determination of lipid accumulation by Oil-Red-O staining
Ações bioquímicas/fisiológicas
Código de classe de armazenamento
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 1
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
Not applicable
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
Not applicable
Equipamento de proteção individual
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Os clientes também visualizaram
Artigos
Information on fatty acid synthesis and metabolism in cancer cells. Learn how proliferatively active cells require fatty acids for functions such as membrane generation, protein modification, and bioenergetic requirements. These fatty acids are derived either from dietary sources or are synthesized by the cell.
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica