M2694
Anti-Munc-18-1 antibody produced in rabbit
IgG fraction of antiserum, buffered aqueous solution
Sinônimo(s):
Anti-Munc-18α, Anti-STXBP1, Anti-Syntaxin-binding protein 1, Anti-rb-Sec-1
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
fonte biológica
rabbit
conjugado
unconjugated
forma do anticorpo
IgG fraction of antiserum
tipo de produto de anticorpo
primary antibodies
clone
polyclonal
Formulário
buffered aqueous solution
peso molecular
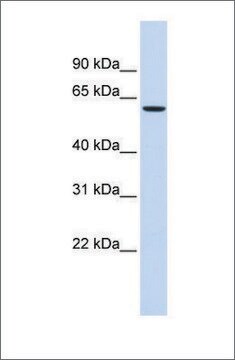
antigen 67 kDa
reatividade de espécies
mouse, rat
técnica(s)
indirect immunofluorescence: 1:250-1:500 using mouse fibroblast NIH3T3 cell line
microarray: suitable
western blot: 1:2,000-1:4,000 using rat brain extract (S1 fraction) and PC12 whole cell extract.
nº de adesão UniProt
Condições de expedição
dry ice
temperatura de armazenamento
−20°C
modificação pós-traducional do alvo
unmodified
Informações sobre genes
human ... STXBP1(6812)
mouse ... Stxbp1(20910)
rat ... Stxbp1(25558)
Descrição geral
Imunogênio
Aplicação
Ações bioquímicas/fisiológicas
forma física
Exoneração de responsabilidade
Não está encontrando o produto certo?
Experimente o nosso Ferramenta de seleção de produtos.
Código de classe de armazenamento
10 - Combustible liquids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 3
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
Not applicable
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
Not applicable
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Certificados de análise (COA)
Não está vendo a versão correta?
Se precisar de uma versão específica, você pode procurar um certificado específico pelo número do lote ou da remessa.
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica