GRSA
Glutathione Reductase Assay Kit
Sufficient for 100 colorimetric tests
Sinônimo(s):
Glutathione Reductase Activity Assay Kit
Faça loginpara ver os preços organizacionais e de contrato
About This Item
Código UNSPSC:
12161503
NACRES:
NA.28
Produtos recomendados
Descrição geral
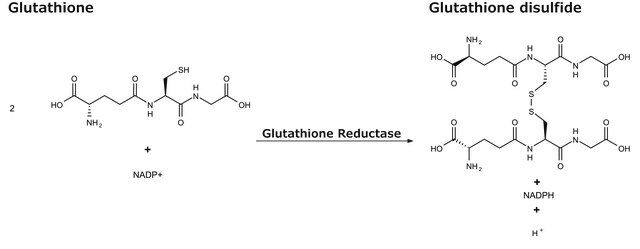
Glutathione reductase (GR) is a ubiquitous enzyme that catalyzes the reduction of oxidized glutathione (GSSG) to glutathione (GSH). Glutathione reductase is essential for the glutathione redox cycle that maintains adequate levels of reduced cellular GSH, which serves as an antioxidant reacting with free radicals and organic peroxides. Glutathione is also a substrate for the glutathione peroxidases and glutathione S-transferases in the detoxification of organic peroxides and the metabolism of xenobiotics.
Aplicação
Glutathione Reductase Assay Kit has been used to measure the activity of glutathione reductase as a part of oxidative stress assessment and also to study the effects of antifouling biocides on it.
Ações bioquímicas/fisiológicas
Glutathione reductase (EC 1.6.4.2) (GR) is a ubiquitous enzyme that catalyzes the reduction of oxidized glutathione (GSSG) to glutathione (GSH). Glutathione reductase is essential for the glutathione redox cycle that maintains adequate levels of reduced cellular GSH, which serves as an antioxidant reacting with free radicals and organic peroxides. Glutathione is also a substrate for the glutathione peroxidases and glutathione S-transferases in the detoxification of organic peroxides and the metabolism of xenobiotics. This kit contains reagents for the spectrophotometric determination of glutathione reductase activity either by following the decrease in absorbance caused by the oxidation of NADPH at 340 nm (UV assay) or the increase in absorption caused by the reduction of dithiobis(2-nitrobenzoic acid) (DTNB) at 412 nm (colorimetric assay). This kit provides reagents for a spectrophotometric assay for measuring the activity of glutathione reductase either by following the decrease in A340 caused by the oxidation of NADPH or the increase in A412 caused by the reduction of dithiobis(2-nitrobenzoic acid).
This kit provides reagents for a spectrophotometric assay for measuring the activity of glutathione reductase either by following the decrease in A340 caused by the oxidation of NADPH or the increase in A412 caused by the reduction of dithiobis(2-nitrobenzoic acid).
Adequação
Suitable for the measurement of glutathione reductase activity in biological samples
Princípio
This kit contains reagents for the spectrophotometric determination of glutathione reductase activity either by following the decrease in absorbance caused by the oxidation of NADPH at 340 nm (UV assay) or the increase in absorption caused by the reduction of dithiobis(2-nitrobenzoic acid) (DTNB) at 412 nm (colorimetric assay). This kit provides reagents for a spectrophotometric assay for measuring the activity of glutathione reductase either by following the decrease in A340 caused by the oxidation of NADPH or the increase in A412 caused by the reduction of dithiobis(2-nitrobenzoic acid).
Nota de análise
UV assay: One unit will cause the oxidation of 1.0 μmole of NADPH at 25 °C at pH 7.5.
Colorimetric assay: One unit will cause the reduction of 1.0 μmole of DTNB to TNB at 25 °C at pH 7.5.
Colorimetric assay: One unit will cause the reduction of 1.0 μmole of DTNB to TNB at 25 °C at pH 7.5.
produto relacionado
Código de classe de armazenamento
10 - Combustible liquids
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
Not applicable
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
Not applicable
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Os clientes também visualizaram
Glutathione: Chemical, Biochemical and Metabolic Aspects.
Dolphin D., et al.
Glutathione: Chemical, Biochemical and Metabolic Aspects (1989)
Justin R Prigge et al.
Cell reports, 19(13), 2771-2781 (2017-06-29)
Energetic nutrients are oxidized to sustain high intracellular NADPH/NADP+ ratios. NADPH-dependent reduction of thioredoxin-1 (Trx1) disulfide and glutathione disulfide by thioredoxin reductase-1 (TrxR1) and glutathione reductase (Gsr), respectively, fuels antioxidant systems and deoxyribonucleotide synthesis. Mouse livers lacking both TrxR1 and
I K Smith et al.
Analytical biochemistry, 175(2), 408-413 (1988-12-01)
A method for assaying glutathione reductase (GSH; EC 1.6.4.2) in crude plant extracts is described. The method is based on the increase in absorbance at 412 nm when 5,5'-dithiobis(2-nitrobenzoic acid) (DTNB) is reduced by GSH. The effects of the following
Effects of antifouling biocides on molecular and biochemical defense system in the gill of the pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas
Mi Seon P, et al.
PLoS ONE, 11(12), e0168978-e0168978 (2016)
V M Factor et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 273(25), 15846-15853 (1998-06-23)
In previous studies we have demonstrated that transforming growth factor (TGF)-alpha/c-myc double transgenic mice exhibit an enhanced rate of cell proliferation, accumulate extensive DNA damage, and develop multiple liver tumors between 4 and 8 months of age. To clarify the
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica