E3910
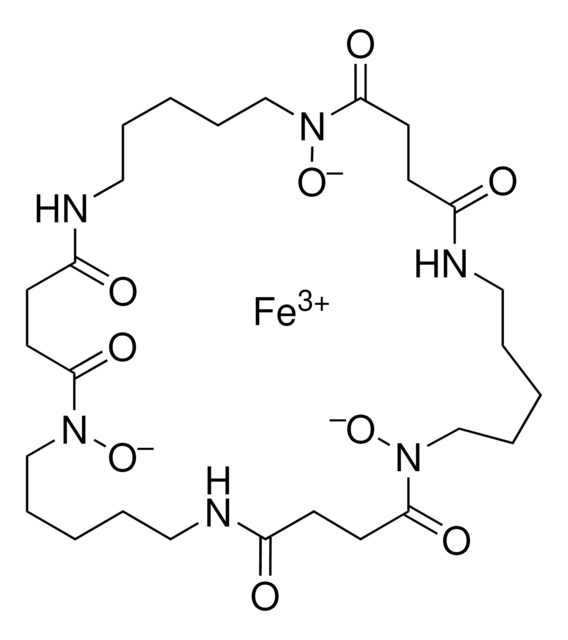
Enterobactin
from Escherichia coli, ≥98% (HPLC)
Sinônimo(s):
Enterochelin
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
fonte biológica
Escherichia coli
Nível de qualidade
Ensaio
≥98% (HPLC)
Condições de expedição
wet ice
temperatura de armazenamento
−20°C
cadeia de caracteres SMILES
N([C@H]2COC(=O)[C@H](COC(=O)[C@H](COC2=O)NC(=O)c4c(c(ccc4)O)O)NC(=O)c3c(c(ccc3)O)O)C(=O)c1c(c(ccc1)O)O
InChI
1S/C30H27N3O15/c34-19-7-1-4-13(22(19)37)25(40)31-16-10-46-29(44)18(33-27(42)15-6-3-9-21(36)24(15)39)12-48-30(45)17(11-47-28(16)43)32-26(41)14-5-2-8-20(35)23(14)38/h1-9,16-18,34-39H,10-12H2,(H,31,40)(H,32,41)(H,33,42)/t16-,17-,18-/m0/s1
chave InChI
SERBHKJMVBATSJ-BZSNNMDCSA-N
Descrição geral
Aplicação
- as a positive control in tryptophan fluorescence quenching experiments
- as a reference standard in high performance liquid chromatography to quantify Kosakonia radicincitans culture medium siderophores
- in the crystallization reservoir to remove iron contamination in the medium and in Fe-enterbactin binding studies
Ações bioquímicas/fisiológicas
produto relacionado
Código de classe de armazenamento
11 - Combustible Solids
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
Not applicable
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
Not applicable
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Os clientes também visualizaram
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica


![(±)-(E)-4-Ethyl-2-[(Z)-hydroxyimino]-5-nitro-3-hexen-1-yl-nicotinamide ≥97%](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/285/524/99543643-31d0-4c4f-b8da-9b1f872868ad/640/99543643-31d0-4c4f-b8da-9b1f872868ad.png)