C8273
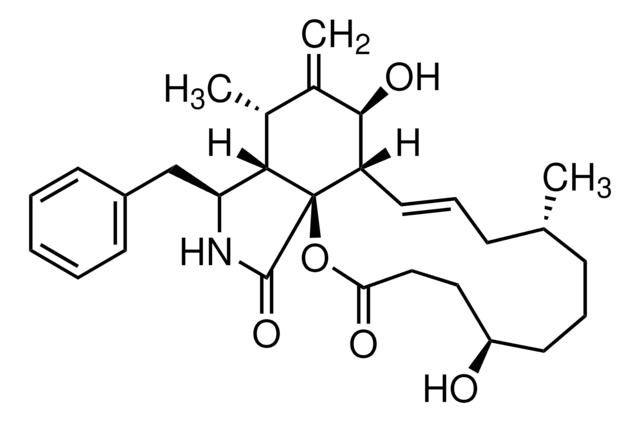
Cytochalasin D
from Zygosporium mansonii, ≥98% (TLC and HPLC), powder
Sinônimo(s):
Lygosporin A, Zygosporin A
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
fonte biológica
Zygosporium mansonii
Nível de qualidade
Ensaio
≥98% (TLC and HPLC)
forma
powder
solubilidade
DMSO: soluble
ethanol: soluble
espectro de atividade do antibiótico
fungi
Modo de ação
DNA synthesis | interferes
temperatura de armazenamento
−20°C
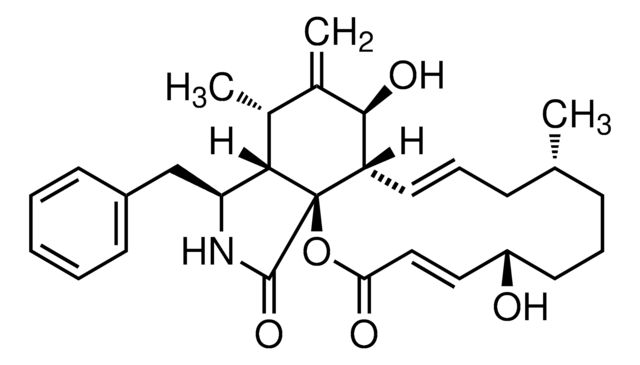
cadeia de caracteres SMILES
[H][C@@]12[C@H](C)C(=C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]3\C=C\C[C@H](C)C(=O)[C@](C)(O)\C=C\[C@@H](OC(C)=O)[C@@]13C(=O)N[C@H]2Cc4ccccc4
InChI
1S/C30H37NO6/c1-17-10-9-13-22-26(33)19(3)18(2)25-23(16-21-11-7-6-8-12-21)31-28(35)30(22,25)24(37-20(4)32)14-15-29(5,36)27(17)34/h6-9,11-15,17-18,22-26,33,36H,3,10,16H2,1-2,4-5H3,(H,31,35)/b13-9+,15-14+/t17-,18+,22-,23-,24+,25-,26+,29+,30+/m0/s1
chave InChI
SDZRWUKZFQQKKV-JHADDHBZSA-N
Procurando produtos similares? Visita Guia de comparação de produtos
Descrição geral
Aplicação
- to treat H9c2 cells to study the relationship between cell stiffness and the F-actin cytoskeleton
- as inhibitor of receptor-mediated endocytosis to treat oligodendrocyte precursor cells (OPCs) to investigate the effect of inhibiting specific extracellular vesicle (EV) uptake pathways
- in in vitro embryo culture to artificially activate oocytes
Ações bioquímicas/fisiológicas
produto relacionado
Palavra indicadora
Danger
Frases de perigo
Declarações de precaução
Classificações de perigo
Acute Tox. 2 Oral
Código de classe de armazenamento
6.1A - Combustible acute toxic Cat. 1 and 2 / very toxic hazardous materials
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 3
Equipamento de proteção individual
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges
Certificados de análise (COA)
Busque Certificados de análise (COA) digitando o Número do Lote do produto. Os números de lote e remessa podem ser encontrados no rótulo de um produto após a palavra “Lot” ou “Batch”.
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Os clientes também visualizaram
Artigos
High titer lentiviral particles including beta-actin, alpha-tubulin and vimentin used for live cell analysis of cytoskeleton structure proteins.
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica