A8949
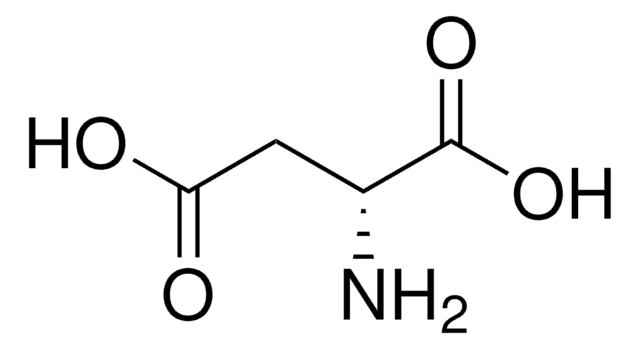
Ácido L-aspártico
≥99% (HPLC), BioXtra
Sinônimo(s):
Ácido (S)-(+)-aminosuccínico, Ácido (S)-aminobutanodioico
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
Nome do produto
Ácido L-aspártico, BioXtra, ≥99% (HPLC)
linha de produto
BioXtra
Ensaio
≥99% (HPLC)
Formulário
powder
Impurezas
≤0.0005% Phosphorus (P)
≤0.1% Insoluble matter
resíduo de ignição
≤0.1%
cor
white to off-white
pf
>300 °C (dec.) (lit.)
solubilidade
1 M HCl: 0.5 M, clear, colorless
traços de ânion
chloride (Cl-): ≤0.05%
sulfate (SO42-): ≤0.05%
traços de cátion
Al: ≤0.0005%
Ca: ≤0.001%
Cu: ≤0.0005%
Fe: ≤0.0005%
K: ≤0.005%
Mg: ≤0.0005%
NH4+: ≤0.05%
Na: ≤0.005%
Pb: ≤0.001%
Zn: ≤0.0005%
cadeia de caracteres SMILES
N[C@@H](CC(O)=O)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C4H7NO4/c5-2(4(8)9)1-3(6)7/h2H,1,5H2,(H,6,7)(H,8,9)/t2-/m0/s1
chave InChI
CKLJMWTZIZZHCS-REOHCLBHSA-N
Informações sobre genes
human ... CA1(759) , CA2(760)
rat ... Grin2a(24409)
Procurando produtos similares? Visita Guia de comparação de produtos
Aplicação
- Metabolomics Analysis Identifies Differential Metabolites as Biomarkers for Acute Myocardial Infarction.: Research identifies key metabolites, including L-Aspartic acid, involved in the metabolic pathways affected during acute myocardial infarction. This study enhances the understanding of biochemical changes during heart attacks, potentially leading to better diagnostic markers (Zhou et al., 2024).
Ações bioquímicas/fisiológicas
Código de classe de armazenamento
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 1
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
Not applicable
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
Not applicable
Equipamento de proteção individual
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Os clientes também visualizaram
Chromatograms
application for HPLCapplication for HPLCNossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica