21750
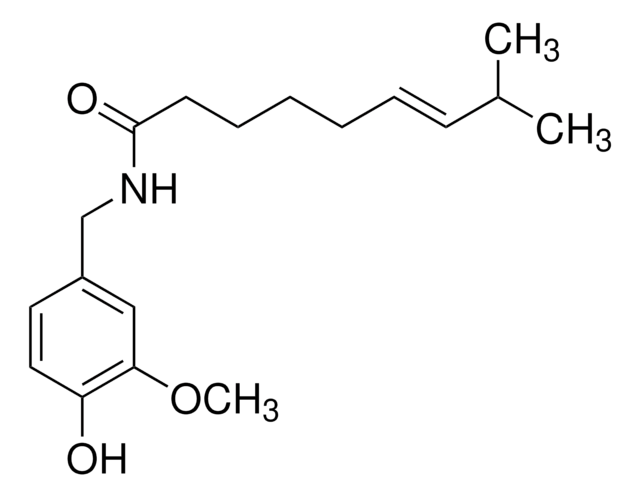
Capsaicin
from Capsicum sp., ≥50% (HPLC)
Sinônimo(s):
8-Methyl-N-vanillyl-trans-6-nonenamide
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
fonte biológica
Capsicum sp.
Nível de qualidade
forma
powder
concentração
≥50% (HPLC)
Impurezas
~35% dihydrocapsaicin
pf
62-65 °C (lit.)
62-66 °C
solubilidade
H2O: insoluble
aplicação(ões)
metabolomics
vitamins, nutraceuticals, and natural products
temperatura de armazenamento
2-8°C
cadeia de caracteres SMILES
COc1cc(CNC(=O)CCCC\C=C\C(C)C)ccc1O
InChI
1S/C18H27NO3/c1-14(2)8-6-4-5-7-9-18(21)19-13-15-10-11-16(20)17(12-15)22-3/h6,8,10-12,14,20H,4-5,7,9,13H2,1-3H3,(H,19,21)/b8-6+
chave InChI
YKPUWZUDDOIDPM-SOFGYWHQSA-N
Informações sobre genes
human ... CYP1A2(1544) , TRPV1(7442)
rat ... Trpv1(83810) , Trpv4(66026)
Procurando produtos similares? Visita Guia de comparação de produtos
Descrição geral
Aplicação
Ações bioquímicas/fisiológicas
Palavra indicadora
Danger
Frases de perigo
Declarações de precaução
Classificações de perigo
Acute Tox. 2 Oral - Eye Dam. 1 - Resp. Sens. 1 - Skin Irrit. 2 - Skin Sens. 1 - STOT SE 3
Órgãos-alvo
Respiratory system
Código de classe de armazenamento
6.1A - Combustible acute toxic Cat. 1 and 2 / very toxic hazardous materials
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 3
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
235.4 °F - closed cup
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
113 °C - closed cup
Equipamento de proteção individual
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type P2 (EN 143) respirator cartridges
Certificados de análise (COA)
Busque Certificados de análise (COA) digitando o Número do Lote do produto. Os números de lote e remessa podem ser encontrados no rótulo de um produto após a palavra “Lot” ou “Batch”.
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica