S7110
ApopTag Fluorescein In Situ Apoptosis Detection Kit
The ApopTag Fluorescein In Situ Apoptosis Detection Kit detects apoptotic cells in situ by the indirect TUNEL method, utilizing an anti-digoxigenin antibody that is conjugated to a Fluorescein reporter molecule.
Sinônimo(s):
Apoptosis detection kit
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
Nível de qualidade
fabricante/nome comercial
ApopTag
Chemicon®
técnica(s)
flow cytometry: suitable
immunocytochemistry: suitable
immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections): suitable
método de detecção
fluorometric
Condições de expedição
dry ice
Descrição geral
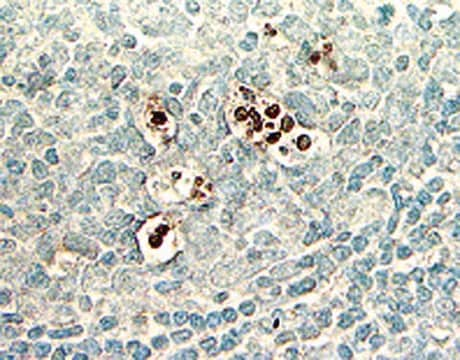
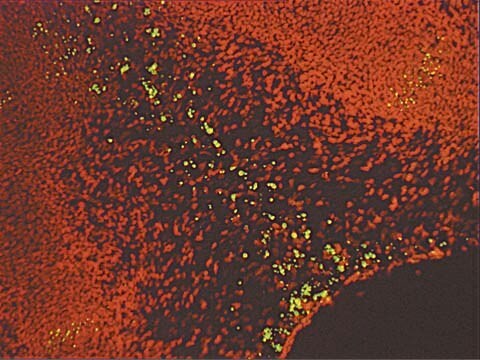
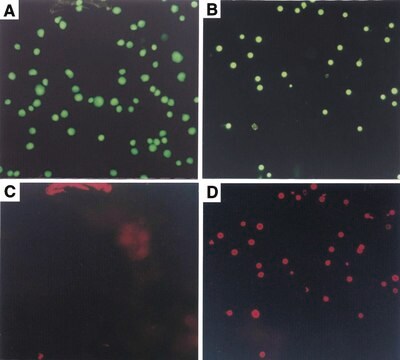
The ApopTag Fluorescein In Situ Apoptosis Detection Kit has been tested for specific staining in these model systems: (a) human normal peripheral blood lymphocytes induced with dexamethasone as stained in cytospins, (b) rat regressing mammary gland as stained in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections, and (c) human leukemic peripheral blood lymphocytes induced with camptothecin, as stained in cell suspensions and used for quantitative flow cytometry.
Aplicação
ApopTag In Situ Apoptosis Detection Kits label apoptotic cells in research samples by modifying genomic DNA utilizing terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT) for detection of positive cells by specific staining. This manual contains information and protocols for the ApopTag Fluorescein In Situ Apoptosis Detection Kit (Catalog number S7110).
Principles of the Procedure
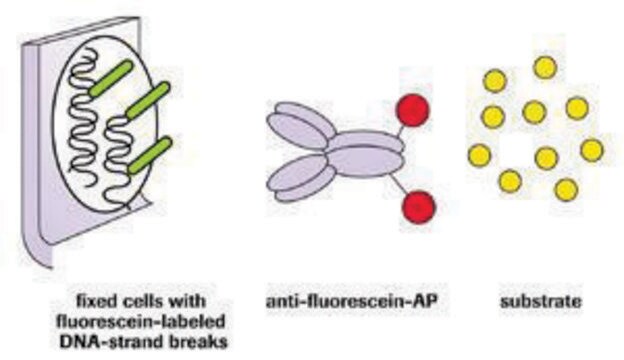
The reagents provided in all ApopTag Kits are designed to label the free 3′OH DNA termini in situ with chemically labeled and unlabeled nucleotides. The nucleotides contained in the Reaction Buffer are enzymatically added to the DNA by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT) (13, 31). TdT catalyzes a template-independent addition of nucleotide triphosphates to the 3′-OH ends of double-stranded or single-stranded DNA. The incorporated nucleotides form an oligomer composed of digoxigenin nucleotide and unlabeled nucleotide in a random sequence. The ratio of labeled to unlabeled nucleotide in ApopTag Kits is optimized to promote anti-digoxigenin antibody binding, or to minimize fluorescein self-quenching. The exact length of the oligomer added has not been measured.
DNA fragments which have been labeled with the digoxigenin-nucleotide are then allowed to bind an anti-digoxigenin antibody that is conjugated to fluorescein (Figure 1A). Fluorescent antibodies provide sensitive detection in immunohistochemistry or immunocytochemistry (i.e. on tissue or cells) and are not subject to experimental variations due to the substrate or the development step. This mixed molecular biological-histochemical systems allows for sensitive and specific staining of very high concentrations of 3′-OH ends that are localized in apoptotic bodies.The ApopTag system differs significantly from previously described in situ labeling techniques for apoptosis (13, 16, 38, 46), in which avidin binding to cellular biotin can be a source of error. The digoxigenin/anti-digoxigenin system has been found to be equally sensitive to avidin/biotin systems (22). Immunochemically-similar ligands for binding of the anti-digoxigenin antibody are generally insignificant in animal tissues, ensuring low background staining. Affinity purified sheep polyclonal antibody is the specific anti-digoxigenin reagent used in ApopTag Kits and exhibits <1% cross-reactivity with the major vertebrate steroids. In addition, the Fc portion of this antibody has been removed by proteolytic digestion to eliminate any non-specific adsorption to cellular Fc receptors.
Componentes
Reaction Buffer 90417 2.0 mL -15°C to -25°C
TdT Enzyme 90418 0.64 mL -15°C to -25°C
Stop/Wash Buffer 90419 20 mL -15°C to -25°C
Blocking Solution 90425 2.6 mL -15°C to -25°C
Anti-Digoxigenin-Fluorescein* 90426 2.1 mL 2°C to 8°C
Plastic Coverslips 90421 100 ea. Room Temp.
*affinity purified sheep polyclonal antibody
Armazenamento e estabilidade
2. Protect the anti-digoxigenin fluorescein antibody (#90426) from unnecessary exposure to light.
Precautions
1. The following kit components contain potassium cacodylate (dimethylarsinic acid) as a buffer: Equilibration Buffer (#90416), Reaction Buffer (#90417), and TdT Enzyme (#90418). These components are harmful if swallowed; avoid contact with skin and eyes (wear gloves, glasses) and wash areas of contact immediately.
2. Antibody Conjugates (#90426) and Blocking Solutions (#90425) contain 0.08% sodium azide as a preservative.
3. TdT Enzyme (#90418) contains glycerol and will not freeze at -20°C. For maximum shelf life, do not warm this reagent to room temperature before dispensing.
Informações legais
Exoneração de responsabilidade
Palavra indicadora
Danger
Frases de perigo
Declarações de precaução
Classificações de perigo
Aquatic Chronic 2 - Carc. 1B - STOT RE 2 Inhalation
Órgãos-alvo
Respiratory Tract
Código de classe de armazenamento
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
Certificados de análise (COA)
Busque Certificados de análise (COA) digitando o Número do Lote do produto. Os números de lote e remessa podem ser encontrados no rótulo de um produto após a palavra “Lot” ou “Batch”.
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Os clientes também visualizaram
Artigos
Cellular apoptosis assays to detect programmed cell death using Annexin V, Caspase and TUNEL DNA fragmentation assays.
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica