EZHGIP
Human GIP ELISA Kit
measures and quantify total GIP levels in 20 μL serum, plasma or cell culture samples
Sinônimo(s):
Gastric inhibitory polypeptide, Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide, Incretin hormone
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
product name
Human GIP (total) ELISA, This Human GIP (total) ELISA is used to measure & quantify GIP levels in Metabolism & Endocrine research.
Nível de qualidade
reatividade de espécies
human
embalagem
kit of 1 × 96 wells
Parâmetros
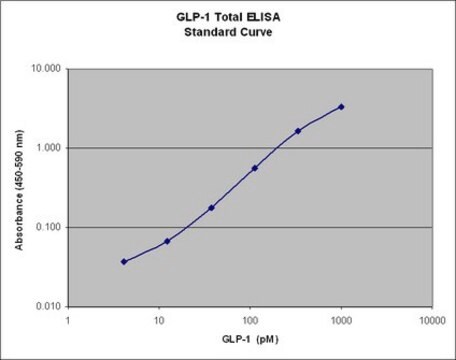
20 μL sample volume (4hr assay)
assay range
accuracy: 86.7%
linearity: 99.9%
sensitivity: 8.2 pg/mL
standard curve range: 8.2-2000 pg/mL
técnica(s)
ELISA: suitable
entrada
sample type cell culture supernatant
sample type serum
sample type plasma (K2 EDTA)
nº de adesão NCBI
nº de adesão UniProt
aplicação(ões)
research use
método de detecção
colorimetric (450nm/590nm)
Condições de expedição
wet ice
temperatura de armazenamento
2-8°C
Informações sobre genes
human ... GNAI2(2771)
Categorias relacionadas
Descrição geral
Aplicação
Outras notas
Exoneração de responsabilidade
Palavra indicadora
Danger
Frases de perigo
Declarações de precaução
Classificações de perigo
Acute Tox. 3 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Chronic 2 - Met. Corr. 1 - Skin Sens. 1
Código de classe de armazenamento
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
Certificados de análise (COA)
Busque Certificados de análise (COA) digitando o Número do Lote do produto. Os números de lote e remessa podem ser encontrados no rótulo de um produto após a palavra “Lot” ou “Batch”.
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica