613560
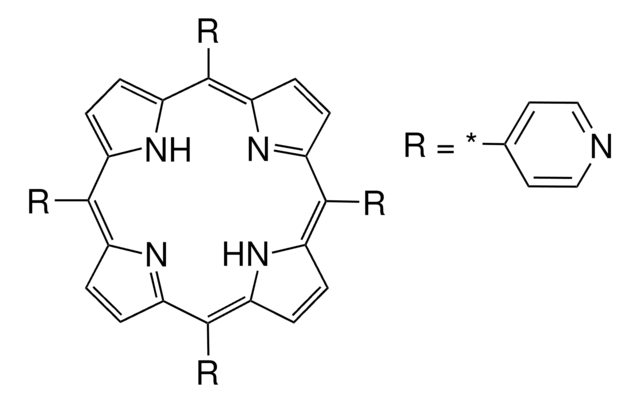
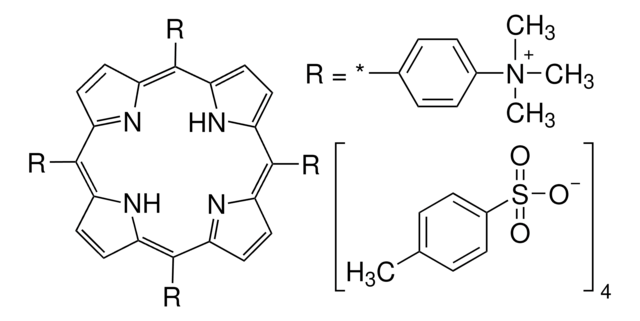
TMPyP4
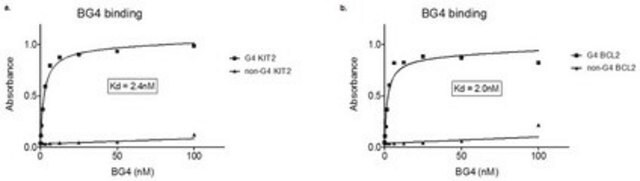
A potent inhibitor of human telomerase (IC₅₀ = 6.5 µM).
Sinônimo(s):
TMPyP4, meso-5,10,15,20-Tetrakis-(N-methyl-4-pyridyl)porphine, Tetratosylate
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
Nível de qualidade
Ensaio
≥90% (TLC)
forma
solid
fabricante/nome comercial
Calbiochem®
condição de armazenamento
OK to freeze
desiccated (hygroscopic)
protect from light
cor
purple
solubilidade
water: 1 mg/mL
Condições de expedição
ambient
temperatura de armazenamento
2-8°C
InChI
1S/C44H37N8.4C7H8O3S/c1-49-21-13-29(14-22-49)41-33-5-7-35(45-33)42(30-15-23-50(2)24-16-30)37-9-11-39(47-37)44(32-19-27-52(4)28-20-32)40-12-10-38(48-40)43(36-8-6-34(41)46-36)31-17-25-51(3)26-18-31;4*1-6-2-4-7(5-3-6)11(8,9)10/h5-28H,1-4H3,(H,45,46,47,48);4*2-5H,1H3,(H,8,9,10)/q+3;;;;/p-3
chave InChI
AKZFRMNXBLFDNN-UHFFFAOYSA-K
Descrição geral
Ações bioquímicas/fisiológicas
Advertência
Outras notas
Izbicka, E., et al. 1999. Cancer Res. 59, 639.
Anantha, N.V., et al. 1998. Biochemistry 37, 2709.
Arthanari, H., et al. 1998. Nucleic Acids Res. 26, 3724.
Wheelhouse, R.T., et al. 1998. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 120, 3261.
Informações legais
Código de classe de armazenamento
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 3
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
Not applicable
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
Not applicable
Certificados de análise (COA)
Busque Certificados de análise (COA) digitando o Número do Lote do produto. Os números de lote e remessa podem ser encontrados no rótulo de um produto após a palavra “Lot” ou “Batch”.
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Os clientes também visualizaram
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica