19-137
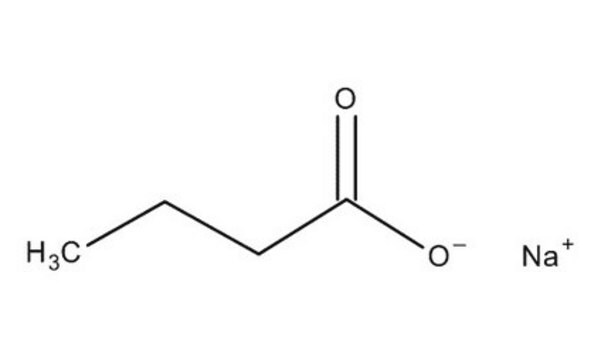
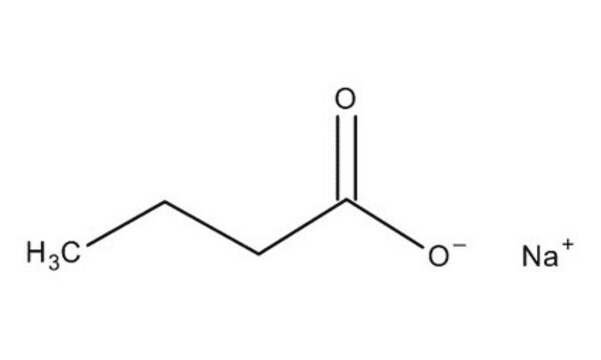
Sodium Butyrate
For use as a histone deacetylase inhibitor.
Sinônimo(s):
Butyric acid sodium salt
Faça loginpara ver os preços organizacionais e de contrato
About This Item
Código UNSPSC:
41116012
eCl@ss:
32160405
NACRES:
NA.41
Produtos recomendados
Nível de qualidade
Formulário
liquid
fabricante/nome comercial
Upstate®
técnica(s)
activity assay: suitable (histone deacetylase (HDAC))
Condições de expedição
wet ice
Aplicação
Sodium Butyrate has been used:
- to inhibit histone deacetylase (HDAC) and study its effect on fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) expression in liver
- to inhibit deacetylase activity in embryonic stem (ES) cells to determine if the enzymatic activity of the mSin3A-HDAC complex is essential for Nanog expression
- as a reagent during tissue homogenization
- as a supplement in chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) dilution buffer
Ações bioquímicas/fisiológicas
Sodium Butyrate is a short-chain fatty acid and a histone deacetylase inhibitor. It protects dopaminergic neuronal cells from α-synuclein mediated transcriptional deregulation and DNA damage, maybe by enhancing the expression of DNA-repair genes. Sodium butyrate may promote the production of foreign proteins such as erythropoietin, tissue plasminogen activator, antibody, and nitric oxide synthase in recombinant Chinese hamster ovary (rCHO) cell cultures. But, the higher concentration of sodium butyrate in rCHO cell cultures may also exhibit a cytotoxic effect on cell growth by inducing apoptosis. Sodium Butyrate prevents the growth of cancer cells by downregulating the thioredoxin 1 (Trx1) expression, stimulating reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, and inhibiting cell proliferation and migration of various carcinoma cells including colorectal cancer (CRC).
forma física
CH3CH2CH2COONa
Armazenamento e estabilidade
1 year at 4°C
Informações legais
UPSTATE is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
Exoneração de responsabilidade
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Palavra indicadora
Warning
Frases de perigo
Declarações de precaução
Classificações de perigo
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2
Código de classe de armazenamento
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 1
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
Not applicable
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
Not applicable
Certificados de análise (COA)
Busque Certificados de análise (COA) digitando o Número do Lote do produto. Os números de lote e remessa podem ser encontrados no rótulo de um produto após a palavra “Lot” ou “Batch”.
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Os clientes também visualizaram
Alba Font-Tello et al.
Nature protocols, 15(8), 2503-2518 (2020-06-28)
Fixed-tissue ChIP-seq for H3K27 acetylation (H3K27ac) profiling (FiTAc-seq) is an epigenetic method for profiling active enhancers and promoters in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissues. We previously developed a modified ChIP-seq protocol (FiT-seq) for chromatin profiling in FFPE. FiT-seq produces high-quality chromatin
Macrophage inflammatory protein-2: chromosomal regulation in rat small intestinal epithelial cells
Ohno, Y, et al
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA, 94, 10279-10284 (1997)
Activation of the mouse cytokeratin A (endo A) gene in teratocarcinoma F9 cells by the histone deacetylase inhibitor Trichostatin A
Miyashita, T, et al
Febs Letters, 353, 225-229 (1994)
No Soo Kim et al.
Biotechnology and bioengineering, 78(2), 217-228 (2002-03-01)
Sodium butyrate (NaBu) can enhance the expression of genes controlled by some of the mammalian promoters, but it can also inhibit cell growth and induce cellular apoptosis. Thus, the beneficial effect of using a higher concentration of NaBu on a
Isabel Paiva et al.
Human molecular genetics, 26(12), 2231-2246 (2017-04-04)
Alpha-synuclein (aSyn) is considered a major culprit in Parkinson's disease (PD) pathophysiology. However, the precise molecular function of the protein remains elusive. Recent evidence suggests that aSyn may play a role on transcription regulation, possibly by modulating the acetylation status
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica