1091108
USP
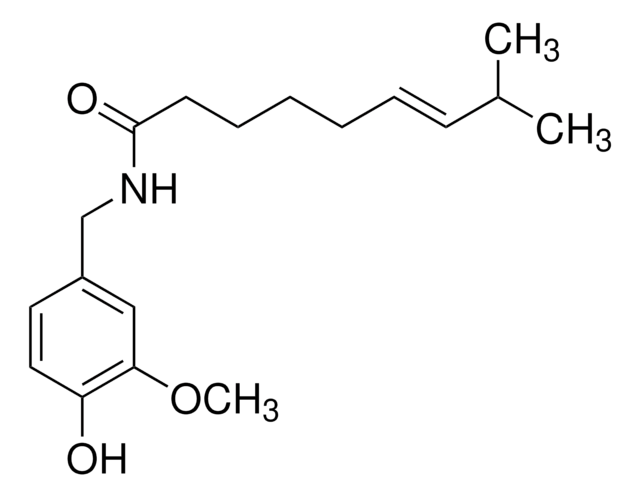
Capsaicin
United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Reference Standard
Synonym(s):
8-Methyl-N-vanillyl-trans-6-nonenamide
About This Item
Recommended Products
grade
pharmaceutical primary standard
API family
capsaicin
manufacturer/tradename
USP
mp
62-65 °C (lit.)
application(s)
pharmaceutical (small molecule)
format
neat
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
COc1cc(CNC(=O)CCCC\C=C\C(C)C)ccc1O
InChI
1S/C18H27NO3/c1-14(2)8-6-4-5-7-9-18(21)19-13-15-10-11-16(20)17(12-15)22-3/h6,8,10-12,14,20H,4-5,7,9,13H2,1-3H3,(H,19,21)/b8-6+
InChI key
YKPUWZUDDOIDPM-SOFGYWHQSA-N
Gene Information
human ... TRPV1(7442)
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Application
Also used to prepare standard solutions for the assay, identification, composition and strength analysis according to the given below monographs of United States Pharmacopeia (USP):
- Capsaicin
- Capsicum Oleoresin
- Capsicum
- Ginger Tincture
Biochem/physiol Actions
Analysis Note
Other Notes
Related product
signalword
Danger
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 2 Oral - Eye Dam. 1 - Resp. Sens. 1 - Skin Irrit. 2 - Skin Sens. 1 - STOT SE 3
target_organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class
6.1A - Combustible acute toxic Cat. 1 and 2 / very toxic hazardous materials
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
235.4 °F - closed cup
flash_point_c
113 °C - closed cup
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service