G6657
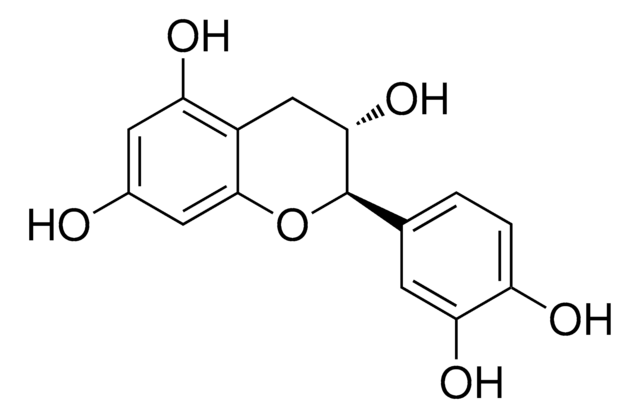
(−)-Gallocatechin
≥98% (HPLC)
Synonym(s):
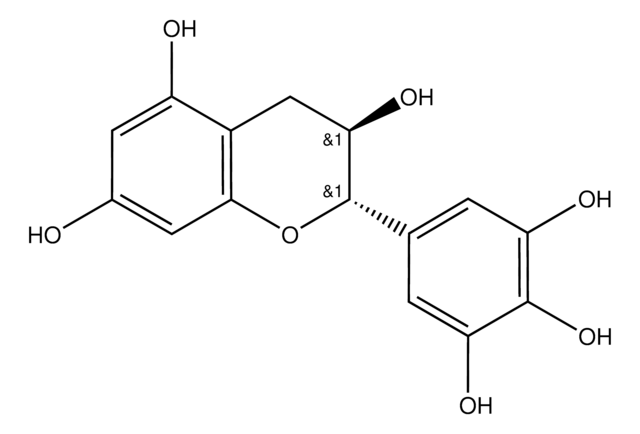
(2S,3R)-2-(3,4,5-Trihydroxyphenyl)-3,4-dihydro-1(2H)-benzopyran-3,5,7-triol
About This Item
Recommended Products
Quality Level
assay
≥98% (HPLC)
solubility
H2O: 5 mg/mL (heat 2-10 min at 105C)
alcohol: soluble
application(s)
metabolomics
vitamins, nutraceuticals, and natural products
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
O[C@@H]1Cc2c(O)cc(O)cc2O[C@H]1c3cc(O)c(O)c(O)c3
InChI
1S/C15H14O7/c16-7-3-9(17)8-5-12(20)15(22-13(8)4-7)6-1-10(18)14(21)11(19)2-6/h1-4,12,15-21H,5H2/t12-,15+/m1/s1
InChI key
XMOCLSLCDHWDHP-DOMZBBRYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Application
- for the identification of phenolic compounds present in Pineapple (Ananas comosus) using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)
- to evaluate the catechin profiles from Camellia sinensis green tea, white tea, and flower sample by high-performance liquid chromatography/photodiode array detection (RP-HPLC/PDAD) analysis
- as a reference standard for the flavan-3-ols profiling muscadine grape hybrid varieties using high-performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole, time-of-flight, tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-qTOF-MS/MS) analysis
Biochem/physiol Actions
Other Notes
signalword
Warning
hcodes
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
target_organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Antioxidants protect biological systems from oxidative damage produced by oxygen-containing free radicals and from redoxactive transition metal ions such as iron, copper, and cadmium.
Related Content
DISCOVER Bioactive Small Molecules for Nitric Oxide & Cell Stress Research
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service