Recommended Products
biological source
wheat
Quality Level
assay
≥75% protein basis
form
solid
technique(s)
surface plasmon resonance (SPR): suitable
General description
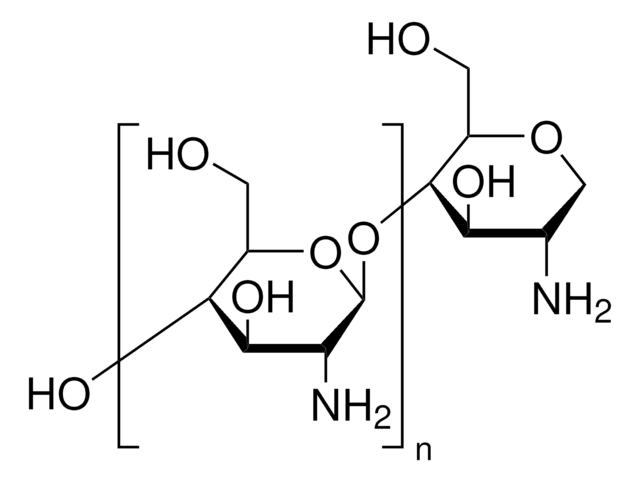
Gluten forms the chief storage protein fraction in a mature wheat grain. Gluten proteins can be divided into three main groups: high molecular weight glutenin subunits (HMW-GS), low molecular weight glutenin subunits (LMW-GS), and gliadins. Gluten has a great impact on the quality of a whole range of cereal-based foods.
Gluten, a cohesive, visco-elastic proteinaceous material, is produced as a by-product of the isolation of starch from wheat flour. It is generally supplied in a dried state called vital wheat gluten.
Application
Gluten from wheat has been used:
- as a source of the total gluten protein to produce a gluten film to assess its viscoelastic properties at the mesostructure level
- to study its effect on metabolic homeostasis in a murine model of diet-induced obesity
- as a nitrogen source in gluten agar/gliadin agar (Glu-A/Gli-A) medium for gluten and gliadin hydrolysis assays
Biochem/physiol Actions
Gluten exhibits visco-elastic properties, which helps in preparing synthetic cheese with the texture and eating quality of natural cheese. It helps in fortifying low-protein bread flours. Gluten is majorly used in non-bakery foods as a meat replacement in vegetarian foods. It is also used in the production of seafood and crab analogs. Vital wheat gluten has a unique visco-elastic property that enhances dough strength, mixing tolerance, and handling properties.
Quality
Crude, ≥ 75% protein
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
B Cuq et al.
Journal of agricultural and food chemistry, 48(7), 2954-2959 (2000-10-14)
Modifications of mechanical properties of wheat dough during thermal treatments depend mainly on the capacity of wheat gluten proteins to establish intra- and intermolecular interactions when subjected to high-temperature processing. The present study investigates the effect of thermal treatments on
Naphtali Qely Remy et al.
microPublication biology, 2022 (2022-10-12)
Gluten sensitivity is associated with digestive and neurological disorders, correlating with abnormal amino acid levels, innate immune responses, gut dysbiosis and movement incoordination. However, the molecular mechanisms linking dietary gluten and brain function remain incompletely understood. We used Drosophila melanogaster
Buket Kunduhoglu et al.
Probiotics and antimicrobial proteins, 13(3), 720-733 (2020-11-11)
Celiac disease (CD) is a chronic autoimmune disease that occurs in genetically predisposed individuals. Gluten-hydrolyzing probiotic bacteria are promising for alleviating symptoms in individuals with CD. Therefore, in this study, the gluten hydrolysis ability and probiotic potential of Lact. brevis
C J Whitehead et al.
Health care management review, 14(3), 65-76 (1989-01-01)
A conceptual and empirical analysis of the strategic vulnerability of HMOs shows that they are strategically vulnerable on the social dimension of stakeholder supportiveness. One of the major implications of this finding is that HMOs' cost leadership strategy cannot be
Johanna O Zeitz et al.
European journal of protistology, 49(3), 389-399 (2013-04-13)
Ciliate protozoa contribute to ruminal digestion and emission of the greenhouse gas methane. Individual species of ciliates co-cultured with mixed prokaryote populations were hypothesized to utilize carbohydrate types differently. In an in vitro batch culture experiment, 0.6 g of pure
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service