E5160
Epidermal Growth Factor from mouse
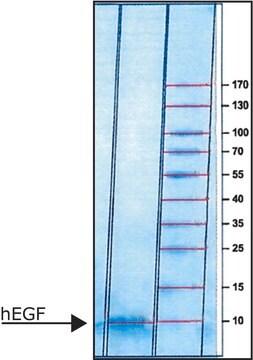
≥90% (SDS-PAGE), recombinant, expressed in E. coli, lyophilized powder, suitable for cell cutlure
Synonym(s):
Mouse EGF, Mouse Epidermal Growth Factor
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(3)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352202
NACRES:
NA.77
Recommended Products
Product Name
Epidermal Growth Factor from mouse, EGF
biological source
mouse
Quality Level
recombinant
expressed in E. coli
assay
≥90% (SDS-PAGE)
form
lyophilized powder
potency
0.05-1 ng/mL ED50/EC50
mol wt
~6 kDa
packaging
pkg of 100 μg
storage condition
avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles
technique(s)
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
impurities
≤1 EU/μg endotoxin (Protein)
color
white
solubility
water: soluble 0.10 mL, clear, colorless
UniProt accession no.
storage temp.
−20°C
Gene Information
mouse ... Egf(13645)
General description
Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF) is a small mitogenic polypeptide (∼6kDa) present in many mammalian species and distributed throughout a wide number of tissues and body fluids. Four ErbB (HER) family receptor tyrosine kinases, including EGFR/ErbB1, ErbB2, ErbB3, and ErbB4 mediate responses to EGF family members. Human and mouse EGFs are very similar, but not identical in their physical and chemical properties. Of the 53 amino acid residues comprising each of the two polypeptides, 37 are common to both molecules, and three disulfide bonds are formed in the same relative positions.
Application
Epidermal Growth Factor from mouse has been used as a basal (N2B27) medium supplement for culturing differentiated mouse embryonic stem (E14) cells.
Biochem/physiol Actions
EGF (epidermal growth factor) is involved in cellular proliferation, differentiation, and survival. Moreover, it was found to affect various biological activities like angiogenesis, inhibition of gastric acid secretion, modulation of the synthesis of a number of hormones, synthesis and turn-over of proteins of the extracellular matrix, calcium release from bone tissue (thus promoting bone resorption), chemoattraction of fibroblasts and epithelial cells, and alone or in combination with other cytokines, mediation of wound healing processes. EGF is mitogenic for a large variety cell types, including fibroblasts, epithelial cells, endothelial cells, chondrocytes, and SV40-3T3 cells.
Physical form
The product is lyophilized from a 0.2 μm-filtered solution of phosphate buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.4.
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 1
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Epidermal growth factor.
Carpenter G and Cohen S
Annual Review of Biochemistry, 48, 193-193 (1979)
Review of epidermal growth factor receptor biology.
Herbst RS
International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics, 59, S21-S21 (2004)
Epidermal growth factor and thyrotropin-releasing hormone act similarly on a clonal pituitary cell strain.
Schonbrunn A et al.
The Journal of Cell Biology, 85, 786-786 (1980)
EGF and TGF-alpha in wound healing and repair.
Schultz G et al.
Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 45, 346-346 (1991)
Ametantrone inhibits prostaglandin-mediated resorption in bone organ culture.
Warner MR et al.
Prostaglandins, 28, 469-469 (1984)
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service