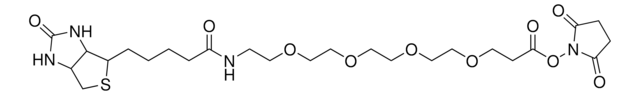
QBD10199
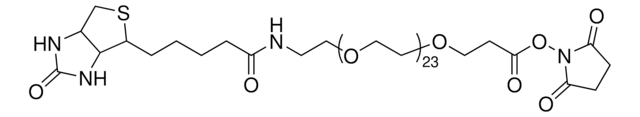
dPEG®4-biotin acid
>95% (HPLC)
Synonym(s):
Biotin-PEG-acid, Biotin-PEG4-COOH, Biotin-PEG4-acid, Carboxy-PEG4-biotin, PEG4-biotin acid
About This Item
Recommended Products
assay
>95% (HPLC)
form
solid or viscous liquid
reaction suitability
reaction type: Biotinylations
reaction type: Pegylations
polymer architecture
shape: linear
functionality: monofunctional
shipped in
ambient
storage temp.
−20°C
Features and Benefits
Automate your Biotin tagging with Synple Automated Synthesis Platform (SYNPLE-SC002)
Legal Information
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
It looks like we've run into a problem, but you can still download Certificates of Analysis from our Documents section.
If you need assistance, please contact Customer Support.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Global Trade Item Number
| SKU | GTIN |
|---|---|
| QBD10199-100MG | 4061842703159 |
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service
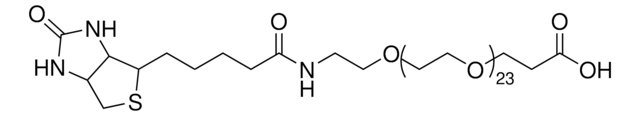
![O-[2-(Biotinyl-amino)ethyl]-O′-(2-carboxyethyl)polyethylene glycol Mp 3,000](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/285/242/a1e6e88b-5b7d-43b5-9bb0-18dcbfdccf43/640/a1e6e88b-5b7d-43b5-9bb0-18dcbfdccf43.png)