推薦產品
生物源
bovine
品質等級
形狀
lyophilized powder
比活性
≥3,000 units/mg protein
分子量
32.5 kDa
成份
Protein, ≥95% biuret
儲存條件
(Store under nitrogen.
Tightly closed. Dry.)
環保替代產品特色
Atom Economy
Design for Energy Efficiency
Use of Renewable Feedstocks
Learn more about the Principles of Green Chemistry.
sustainability
Greener Alternative Product
技術
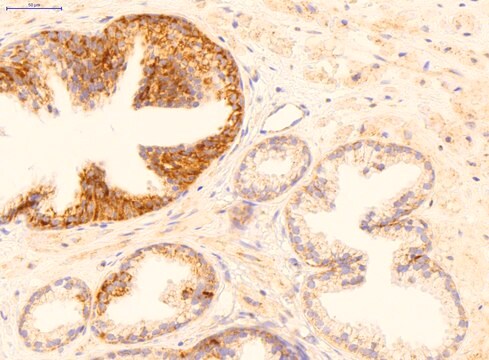
immunoblotting: suitable
inhibition assay: suitable
顏色
blue-green
pI
4.95
溶解度
water: 20 mg/mL
aqueous buffer, pH 7.5: soluble
應用
diagnostic assay manufacturing
環保替代類別
儲存溫度
−20°C
基因資訊
cow ... SOD1(281495) , SOD2(281496)
尋找類似的產品? 前往 產品比較指南
相關類別
一般說明
超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)是一种具有氧化还原活性的金属酶,在有氧和厌氧生物体内均有表达。牛超氧化物歧化酶或CuZn SOD是一种同源二聚体,每个亚基含有一个锌离子和一个铜离子。
應用
- 在一项研究评估辐射诱导失活的超氧化物歧化酶在一氧化二氮饱和溶液中的动力学模型
- 研究超氧阴离子参与肠色氨酸2,3-双加氧酶反应的可能性
- 调查其对人红细胞溶血率及红细胞血红蛋白-一氧化氮复合物(HbNO)稳定性的影响
- 联合过氧化氢酶体外研究其对细胞分化的影响
- 通过化学发光和细胞色素C还原法量化超氧化物水平,研究其对小鼠肺动脉反应性的影响
生化/生理作用
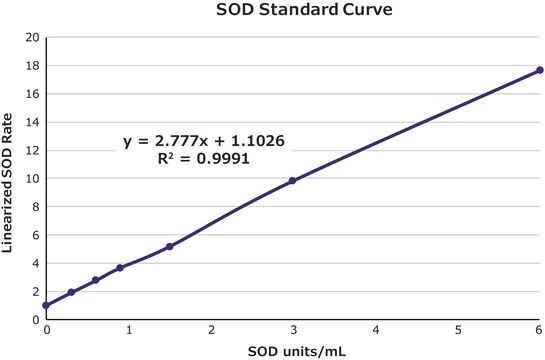
單位定義
外觀
應用
訊號詞
Danger
危險聲明
危險分類
Resp. Sens. 1
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 1
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
個人防護裝備
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
分析證明 (COA)
輸入產品批次/批號來搜索 分析證明 (COA)。在產品’s標籤上找到批次和批號,寫有 ‘Lot’或‘Batch’.。
客戶也查看了
文章
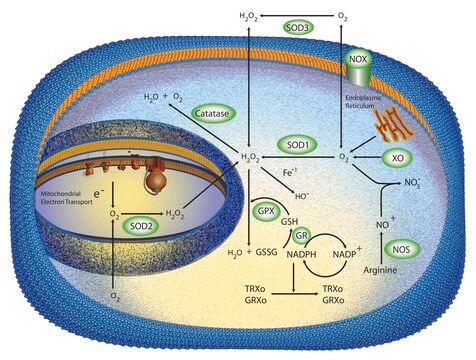
Oxidative stress is mediated, in part, by reactive oxygen species produced by multiple cellular processes and controlled by cellular antioxidant mechanisms such as enzymatic scavengers or antioxidant modulators. Free radicals, such as reactive oxygen species, cause cellular damage via cellular.
條款
Enzymatic Assay of Superoxide Dismutase
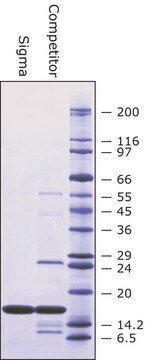
Separation of Superoxide dismutase
Chromatograms
application for HPLC我們的科學家團隊在所有研究領域都有豐富的經驗,包括生命科學、材料科學、化學合成、色譜、分析等.
聯絡技術服務