推薦產品
生物源
bovine liver
品質等級
形狀
lyophilized powder
比活性
2,000-5,000 units/mg protein
分子量
tetramer ~250 kDa
等電點
5.4
UniProt登錄號
運輸包裝
wet ice
儲存溫度
−20°C
InChI
1S/C9H10O3/c1-2-12-9(11)7-3-5-8(10)6-4-7/h3-6,10H,2H2,1H3
InChI 密鑰
NUVBSKCKDOMJSU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
基因資訊
cow ... CAT(280743)
尋找類似的產品? 前往 產品比較指南
一般說明
Research Area: Cell Signaling
Catalase from bovine liver is a tetramer consisting of 4 equal subunits each with a 60 kDa molecular weight. Each of these subunits contains iron bound to a protoheme IX group. The enzyme will also strongly bind to NADP, where NADP and the heme group are within 13.7 angstroms.
Catalase from bovine liver is a tetramer consisting of 4 equal subunits each with a 60 kDa molecular weight. Each of these subunits contains iron bound to a protoheme IX group. The enzyme will also strongly bind to NADP, where NADP and the heme group are within 13.7 angstroms.
應用
过氧化氢酶作为天然抗氧化剂,可用于研究活性氧物质对基因表达和凋亡的作用。它还被用于保护蛋白质、脂质和核酸免受氧化损伤。 工业上,过氧化氢酶已被用于去除添加至牛奶和奶酪中以及纺织品漂白使用的过氧化氢,并用于检查其对DNA修复大肠杆菌突变体活力的阳性效应。
生化/生理作用
本品不需要任何活化剂,但其活性可被3-氨基-1-H-1,2,4三唑、氰化物、叠氮化物、羟胺、溴化氰、2-巯基乙醇、二硫苏糖醇、邻联茴香胺和硝酸盐抑制。
Catalase, an antioxidant enzyme found in all aerobic organisms, catalyzes the degradation of hydrogen peroxide, a byproduct of metabolic processes, into less harmful water and oxygen. It can also react with alkylhydrogen peroxides, such as methylperoxide and ethylperoxide and the second H2O2 molecule can be replaced by methanol, ethanol, propanol, formate and nitrate as a hydrogen donor. Catalase enzyme uses either iron (Fe) or manganese (Mn) as cofactor, and are classified as Fe-CAT or Mn-CAT.
注意
过氧化氢酶溶液不可冷冻。 冷冻溶液将导致酶活性损失50-70%。
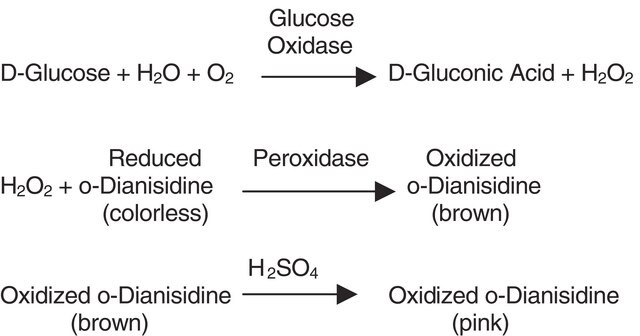
單位定義
一单位酶可在pH7.0、25℃下每分钟分解1.0 μM的H2O2,通过测量A240的下降速率可知H2O2浓度从10.3降至9.2 mM。
準備報告
该产品是一种冻干粉,活性是2,000-5,000单位/mg。
该酶溶于50 mM磷酸钾缓冲液中,浓度为1 mg/mL,pH 7.0。
该酶溶于50 mM磷酸钾缓冲液中,浓度为1 mg/mL,pH 7.0。
儲存和穩定性
Solutions of catalase should not be frozen. Freezing catalase solutions will lead to a loss of activity by 50-70%. The recommended storage temperature of the product in its powdered form is at -20 °C.
抑制劑
產品號碼
描述
訂價
訊號詞
Danger
危險聲明
危險分類
Resp. Sens. 1
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 1
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
個人防護裝備
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
客戶也查看了
Julie Elizabeth Keeble et al.
Pain, 141(1-2), 135-142 (2008-12-09)
Inflammatory diseases associated with pain are often difficult to treat in the clinic due to insufficient understanding of the nociceptive pathways involved. Recently, there has been considerable interest in the role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in inflammatory disease, but
Christopher Gell et al.
Methods in cell biology, 95, 221-245 (2010-05-15)
In vitro assays that reconstitute the dynamic behavior of microtubules provide insight into the roles of microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs) in regulating the growth, shrinkage, and catastrophe of microtubules. The use of total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy with fluorescently labeled tubulin
James C Dooley et al.
Current biology : CB, 30(12), 2404-2410 (2020-05-16)
Cortical development is an activity-dependent process [1-3]. Regarding the role of activity in the developing somatosensory cortex, one persistent debate concerns the importance of sensory feedback from self-generated movements. Specifically, recent studies claim that cortical activity is generated intrinsically, independent
Ahmet H Kaya et al.
Brain research, 1221, 93-97 (2008-06-21)
Serotonin (5-HT) containing neurons in the dorsal raphe nucleus (DRN) may play important roles in Parkinson's disease (PD). This study investigated neural and metabolic activity of the DRN in animal PD models based on dopamine depletion. The data show both
Amol Aher et al.
Developmental cell, 46(1), 40-58 (2018-06-26)
The dynamic instability of microtubules plays a key role in controlling their organization and function, but the cellular mechanisms regulating this process are poorly understood. Here, we show that cytoplasmic linker-associated proteins (CLASPs) suppress transitions from microtubule growth to shortening
文章
Oxidative stress is mediated, in part, by reactive oxygen species produced by multiple cellular processes and controlled by cellular antioxidant mechanisms such as enzymatic scavengers or antioxidant modulators. Free radicals, such as reactive oxygen species, cause cellular damage via cellular.
我們的科學家團隊在所有研究領域都有豐富的經驗,包括生命科學、材料科學、化學合成、色譜、分析等.
聯絡技術服務