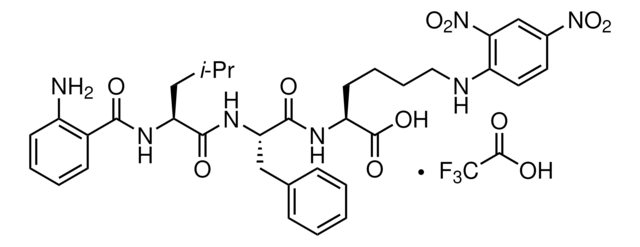
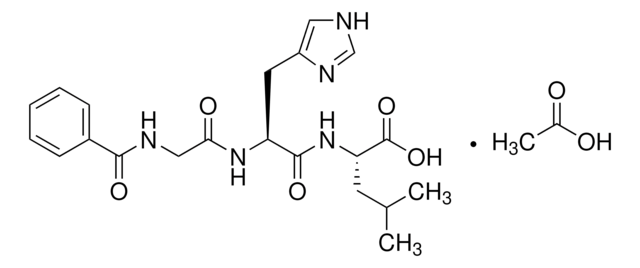
推薦產品
用途
sufficient for 200 fluorometric tests
運輸包裝
dry ice
儲存溫度
−20°C
一般說明
试剂盒中的 ACE 阳性对照可用于筛选 ACE 抑制剂。该试剂盒的 ACE 活性线性范围为 1.5-110 mU。
血管紧张素转换酶(ACE)是肾素-血管紧张素系统(RAS)的关键组分,因其在调节血压、电解质平衡和血管重塑方面的作用而广为人知 1,2 。ACE 主要位于肺的毛细血管中,但也存在于内皮细胞和肾上皮细胞中 3。这种激素系统还可调节体液量。肾素通过从血管紧张素原中裂解几个氨基酸而产生血管紧张素 I。然后 ACE 水解血管紧张素 I 以产生活性血管紧张素 II。血管紧张素 II 还刺激肾上腺皮质分泌醛固酮,通过刺激肾脏的钠重吸收也会导致血压升高 1。由于 ACE 对 RAS 具有重要的调节作用,因此抑制 ACE 已成为用于治疗心血管疾病(如高血压、心力衰竭和糖尿病肾病)的一种有前景的药物靶点。
检测范围:ACE 活性 1.5-110 mU。
應用
- 检测组织/细胞裂解液、血清、血浆中的 ACE1 活性
- 可以筛选 ACE 抑制剂
特點和優勢
我们经济的 ACE 试剂盒还可以帮您节省时间和精力:
- 用于测量各种样品(如血清和血浆)中的 ACE 水平的一种简单、快速、灵敏且直接的方法
- 可以筛选 ACE 抑制剂
- 支持性计算器(点击此处下载计算器 excel 文件):根据您的实验需要计算所需的试剂,并根据您的实验数据分析您的结果!
- 用户友好: 无需称量或混合多种试剂
- 快速指示台卡 - 确保您的实验成功
- 一个试剂盒可完成更多实验 - 包含的试剂足够进行 200 次检测。
單位定義
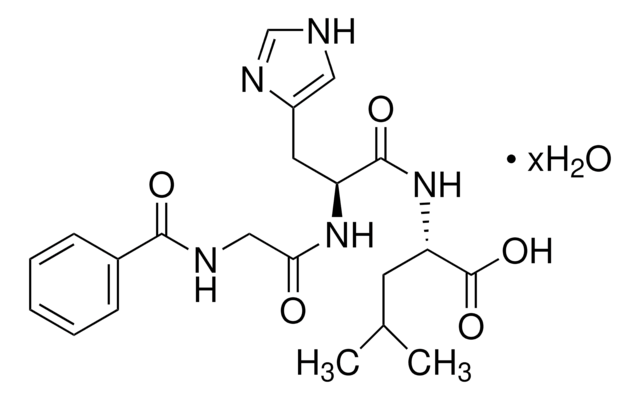
一个单位的 ACE 定义为:在测定条件下,在 37℃ 下,在 1 分钟内从底物释放 1nmol 荧光产物的酶量。该试剂盒含有的试剂足够进行 200 次检测。
儲存類別代碼
10 - Combustible liquids
閃點(°F)
188.6 °F
閃點(°C)
87 °C
分析證明 (COA)
輸入產品批次/批號來搜索 分析證明 (COA)。在產品’s標籤上找到批次和批號,寫有 ‘Lot’或‘Batch’.。
客戶也查看了
Mitja M Zdouc et al.
Cell chemical biology, 28(5), 733-739 (2020-12-16)
Microbial natural products impress by their bioactivity, structural diversity, and ingenious biosynthesis. While screening the less exploited actinobacterial genus Planomonospora, two cyclopeptides were discovered, featuring an unusual Tyr-His biaryl bridging across a tripeptide scaffold, with the sequences N-acetyl-Tyr-Tyr-His and N-acetyl-Tyr-Phe-His.
Flavia L Martins et al.
Bioscience reports, 41(12) (2021-11-10)
The angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE)/Angiotensin II (Ang II) and angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2)/angiotensin-(1-7) (Ang-(1-7)) pathways are coexpressed in most tissues. The balance between these pathways determines, at least in part, whether tissue damage will occur in response to pathological stimuli. The
Guru Prasad Sharma et al.
International journal of radiation oncology, biology, physics, 113(1), 177-191 (2022-01-31)
Radiation-induced lung injury is a major dose-limiting toxicity for thoracic radiation therapy patients. In experimental models, treatment with angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors mitigates radiation pneumonitis; however, the mechanism of action is not well understood. Here, we evaluate the direct
Jorge L Díaz-Gómez et al.
Molecules (Basel, Switzerland), 25(22) (2020-11-25)
In this study, we characterized three novel peptides derived from the 19 kDa α-zein, and determined their bioactive profile in vitro and developed a structural model in silico. The peptides, 19ZP1, 19ZP2 and 19ZP3, formed α-helical structures and had positive
Pradeep K Singh et al.
Neurobiology of disease, 139, 104833-104833 (2020-03-17)
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is characterized by the presence of proteinaceous brain deposits, brain atrophy, vascular dysfunction, and chronic inflammation. Along with cerebral inflammation, peripheral inflammation is also evident in many AD patients. Bradykinin, a proinflammatory plasma peptide, is also linked
我們的科學家團隊在所有研究領域都有豐富的經驗,包括生命科學、材料科學、化學合成、色譜、分析等.
聯絡技術服務