推薦產品
生物源
bacterial (Proteus vulgaris)
品質等級
共軛
(Glucosaminoglycan)
形狀
lyophilized powder
比活性
50-250 units/mg protein
分子量
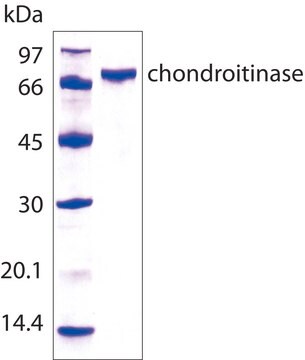
120 kDa by gel filtration
成份
Protein, ~10% Lowry
溶解度
0.01% bovine serum albumin aqueous (BSA) solution: soluble
應用
diagnostic assay manufacturing
異物活動
protease, essentially free
儲存溫度
−20°C
尋找類似的產品? 前往 產品比較指南
相關類別
應用
该酶已被用于研究采用成年大鼠脑细胞,硫酸软骨素蛋白多糖所诱导的发急性、长期变化的后果。以新鲜牛角膜基质为原料,采用软骨素酶ABC对氨基聚糖进行酶解,测定了其在角质细胞培养中的含量。
生化/生理作用
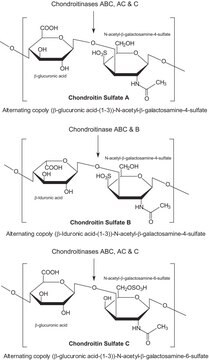
硫酸软骨素酶ABC催化含有(1-4)-β-D-己糖胺基和(1-3)-β-葡聚糖或(1-3)-α-葡聚糖-L-iduronosyl与含有4-脱氧-β-D-葡聚糖-4-enuronosyl基团的双糖链接的清除性降解。它作用于4-硫酸软骨素、6-硫酸软骨素和皮肤硫酸软骨素,缓慢作用于透明质酸盐。分子量约为120 kDa,含有2个不相同的亚基,分子量分别为86 kDa和32 kDa。找到的最佳pH值与硫酸软骨素为8.0,与透明质酸为6.8,以及最佳温度是37°C。以1 mM Zn2+ 为抑制剂,0.05 M醋酸盐为酶的激活剂。
包裝
基于硫酸软骨素 C活性包装。
單位定義
在37°C、pH 8.0条件下,一单位每分钟将释放1.0 μmole的2-乙酰氨基-2-脱氧-3-O-(β-D-葡萄糖)-4-烯-吡喃糖醛糖醛酸)-4-O-磺基-D-半乳糖的混合物和1.0 μmole来自鲨鱼软骨硫酸软骨素的2-乙酰氨基-2-脱氧-3-O-(β-D-葡萄糖-4-烯-吡喃糖醛糖醛酸)-6-O-磺基-D-半乳糖。
準備報告
亲和纯化
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
個人防護裝備
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
分析證明 (COA)
輸入產品批次/批號來搜索 分析證明 (COA)。在產品’s標籤上找到批次和批號,寫有 ‘Lot’或‘Batch’.。
客戶也查看了
Susan M Smith et al.
International journal of molecular sciences, 20(3) (2019-01-27)
The aim of this study was to assess if the ovine articular cartilage serine proteinase inhibitors (SPIs) were related to the Kunitz inter-α-trypsin inhibitor (ITI) family. Ovine articular cartilage was finely diced and extracted in 6 M urea and SPIs
Elizabeth J Bradbury et al.
Brain research bulletin, 84(4-5), 306-316 (2010-07-14)
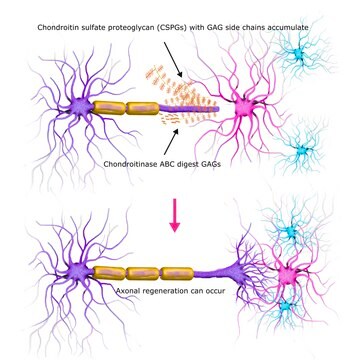
Chondroitin sulphate proteoglycans (CSPGs) are potent inhibitors of growth in the adult CNS. Use of the enzyme chondroitinase ABC (ChABC) as a strategy to reduce CSPG inhibition in experimental models of spinal cord injury has led to observations of a
P N Bansal et al.
Osteoarthritis and cartilage, 18(2), 184-191 (2009-10-10)
An early hallmark of osteoarthritis (OA) is the progressive loss of glycosaminoglycans (GAGs), the extracellular matrix (ECM) component of articular cartilage that confers it with compressive stiffness. Our aim in this work is to establish the feasibility of using Contrast
Rong-Rong Zhao et al.
Neuroscience bulletin, 29(4), 477-483 (2013-07-11)
After spinal cord injury (SCI), re-establishing functional circuitry in the damaged central nervous system (CNS) faces multiple challenges including lost tissue volume, insufficient intrinsic growth capacity of adult neurons, and the inhibitory environment in the damaged CNS. Several treatment strategies
Elizabeth J Bradbury et al.
Nature, 416(6881), 636-640 (2002-04-12)
The inability of axons to regenerate after a spinal cord injury in the adult mammalian central nervous system (CNS) can lead to permanent paralysis. At sites of CNS injury, a glial scar develops, containing extracellular matrix molecules including chondroitin sulphate
文章
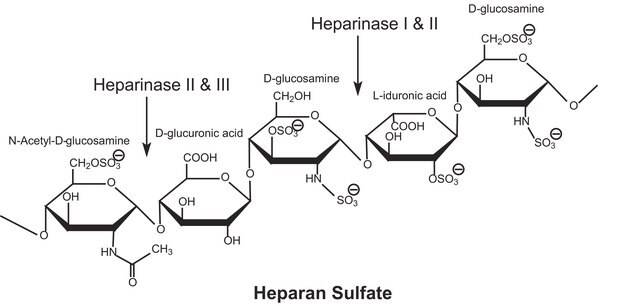
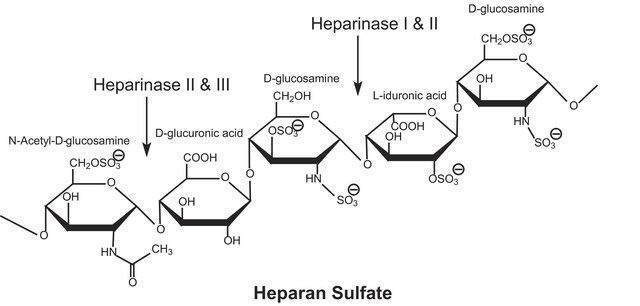
Glycosaminoglycans are large linear polysaccharides constructed of repeating disaccharide units.
我們的科學家團隊在所有研究領域都有豐富的經驗,包括生命科學、材料科學、化學合成、色譜、分析等.
聯絡技術服務