推荐产品
生物源
Escherichia coli ( H 560 pol A1)
品質等級
化驗
100%
形狀
solution
比活性
~40000 units/mg protein
包裝
pkg of 100 U
製造商/商標名
Roche
技術
cDNA synthesis: suitable
顏色
colorless
最適pH
7.5-9.1
溶解度
water: miscible
適合性
suitable for molecular biology
NCBI登錄號
應用
life science and biopharma
異物活動
RNase, none detected (up to 10 U with MS- II- RNA)
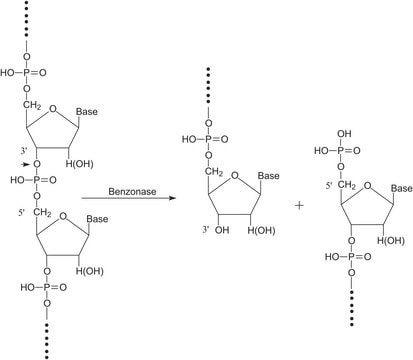
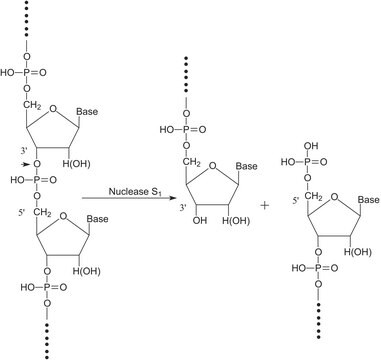
endonuclease ~10 units, none detected (using lambda-DNA)
nicking activity 10 units, none detected
運輸包裝
dry ice
儲存溫度
−20°C (−15°C to −25°C)
基因資訊
Escherichia coli ... rnhA(946955)
一般說明
核糖核酸酶H(RNA酶H)是一种位于细胞核与细胞质中的非特异性核糖核酸内切酶,。它普遍存在并广泛分布于病毒和人类等多种生物中。
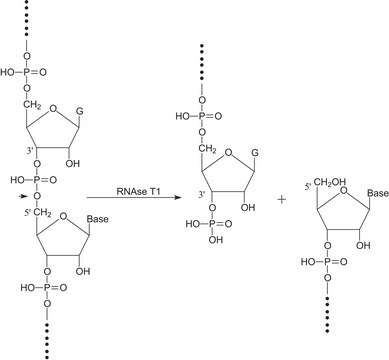
非(序列)专一性核糖核酸内切酶,可特异性地水解RNA:DNA杂合链中的RNA链。需要至少4个连续碱基对(RNA:DNA)才能发挥酶活性。RNase H可切割RNA释放出5′-寡聚核糖核苷酸。
来源:大肠杆菌H560 pol A1
存储液:25 mM Tris-HCl,50 mM KCl,1 mM 二硫苏糖醇,0.1 mM EDTA,50% 甘油 (v/v),pH 8.0 (+ 4°C)
单位体积活力:1 x 103 U/ml,按照Hillenbrand & Staudenbauer法分析。
来源:大肠杆菌H560 pol A1
存储液:25 mM Tris-HCl,50 mM KCl,1 mM 二硫苏糖醇,0.1 mM EDTA,50% 甘油 (v/v),pH 8.0 (+ 4°C)
单位体积活力:1 x 103 U/ml,按照Hillenbrand & Staudenbauer法分析。
應用
核糖核酸酶 H (RNase H) 已用于:
- 体内 RNA 引发的 DNA 合成初始化
- 第二链 cDNA 合成过程中 mRNA 消除
- RNA 的位点特异性切割
- 检测天然来源的双链DNA中的RNA:DNA区域
- 如果存在 oligo (dT),则去除 mRNA 的 poly (A) 序列
- RNA提取和定量逆转录聚合酶链式反应(RT-PCR)
生化/生理作用
核糖核酸酶H(RNA酶H)特异性剪切RNA:DNA杂交体中的RNA。需要至少4个连续碱基对(RNA:DNA)才能发挥酶活性。RNase H可切割RNA释放出5′-寡核糖核苷酸。RNase H与核酸免疫有关。用RNase H降解mRNA,可消去80%的mRNA和蛋白表达。RNase H识别起始密码子和3′和5′端未翻译区。该酶参与DNA复制。
特點和優勢
- 消除潜在的PCR误差来源。
- 在后续PCR过程中增加引物的可结合性。
品質
无核酸内切酶、核糖核酸酶和切割活性。
單位定義
RNase H活性已按照Hillenbrand与Staudenbauer方法进行分析。一单位RNase H的定义为,在+37 °C的标准分析下,通过[3H] poly(A) x poly(dT) 在20分钟时间内生成1 nmol酸性可溶核糖核苷酸所需的酶量。
体积活性:约1 U/μl
体积活性:约1 U/μl
準備報告
激活剂:此酶在巯基试剂存在的条件下拥有最高活性
儲存和穩定性
-15–-25 °C下储存(未开封)
其他說明
仅用于生命科学研究。不可用于诊断。在cDNA合成步骤之后使用RNase H能够提升两步法RT-PCR分析的灵敏性。
儲存類別代碼
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 1
閃點(°F)
does not flash
閃點(°C)
does not flash
其他客户在看
Amandine Bonnet et al.
Molecular cell, 67(4), 608-621 (2017-08-02)
Transcription is a source of genetic instability that can notably result from the formation of genotoxic DNA:RNA hybrids, or R-loops, between the nascent mRNA and its template. Here we report an unexpected function for introns in counteracting R-loop accumulation in
Antisense oligonucleotides and rna interference
Kher G, et al.
Chalcogenide Lett null
β-catenin activity in late hypertrophic chondrocytes locally orchestrates osteoblastogenesis and osteoclastogenesis.
Houben A, et al.
Development, dev-137489 (2016)
David A Ellis et al.
PLoS genetics, 17(8), e1009784-e1009784 (2021-09-01)
Aberrant repair of DNA double-strand breaks can recombine distant chromosomal breakpoints. Chromosomal rearrangements compromise genome function and are a hallmark of ageing. Rearrangements are challenging to detect in non-dividing cell populations, because they reflect individually rare, heterogeneous events. The genomic
Anirudh Chakravarthy et al.
Life science alliance, 4(12) (2021-10-02)
The continued resurgence of the COVID-19 pandemic with multiple variants underlines the need for diagnostics that are adaptable to the virus. We have developed toehold RNA-based sensors across the SARS-CoV-2 genome for direct and ultrasensitive detection of the virus and
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门