T5168
Monoclonal Anti-α-Tubulin antibody produced in mouse

ascites fluid, clone B-5-1-2
Synonym(s):
Alpha Tubulin Antibody Sigma, Anti Tubulin Sigma, Tubulin Antibody Sigma, Tubulin Antibody Sigma - Monoclonal Anti-α-Tubulin antibody produced in mouse
About This Item
Recommended Products
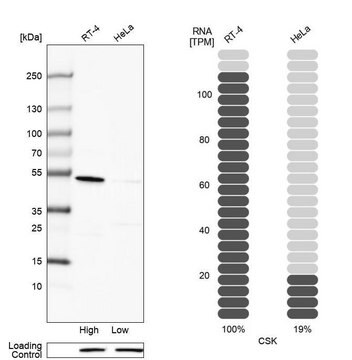
biological source
mouse
Quality Level
conjugate
unconjugated
antibody form
ascites fluid
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
B-5-1-2, monoclonal
mol wt
antigen ~50 kDa
contains
15 mM sodium azide
species reactivity
mouse, chicken, Chlamydomonas, African green monkey, human, rat, bovine, sea urchin, kangaroo rat
enhanced validation
independent ( Antibodies)
Learn more about Antibody Enhanced Validation
technique(s)
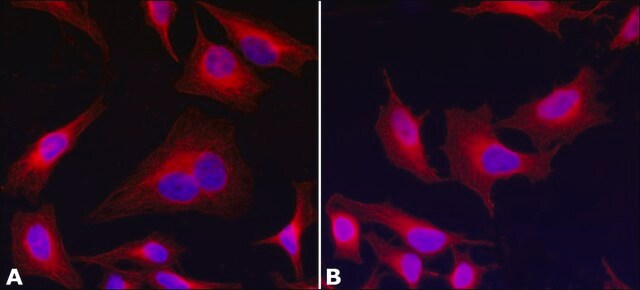
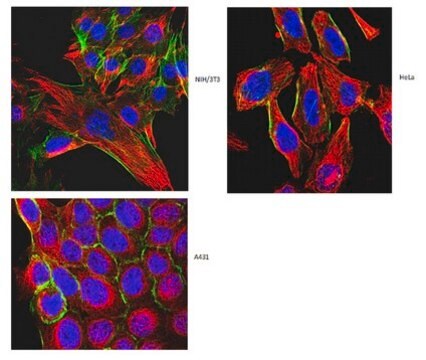
indirect immunofluorescence: 1:2,000 using cultured human or chicken fibroblasts
radioimmunoassay: suitable
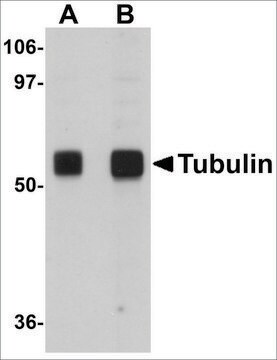
western blot: 1:4,000 using human fibroblast cell extract
isotype
IgG1
UniProt accession no.
application(s)
research pathology
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
target post-translational modification
unmodified
Gene Information
human ... TUBA4A(7277)
mouse ... Tuba1a(22142)
rat ... Tuba1a(64158)
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Specificity
Immunogen
Application
- In immunofluorescence Analysis
- In western blotting/ Immunoblotting
- For immunolabelling cells in electron microscopy
Biochem/physiol Actions
α-Tubulin is a key regulator of cytoskeletal proteins. It mediates cellular developmental stages such as proliferation, migration, signalling and also maintains the shape of the cell. α-Tubulin controls trafficking, signaling and cellular tensegrity mediated by microtubules. The encoded protein is associated with the development and progression of cancer. α-Tubulin acetylation potentiates the metastatic property of breast cancer. Mutation in TUBA4A is associated with the development of various types of cancers, such as oral cancer, breast cancer, rectal cancer, lung cancer and prostate cancer. In addition, variation in the TUBA4A leads to sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
Microtubules function as structural and mobile elements in mitosis, intracellular transport, flagellar movement and the cytoskeleton.
Physical form
Storage and Stability
Disclaimer
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
Storage Class
10 - Combustible liquids
wgk_germany
WGK 1
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Microtubules of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton are composed of a heterodimer of α- and β-tubulin. In addition to α-and β-tubulin, several other tubulins have been identified, bringing the number of distinct tubulin classes to seven.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service