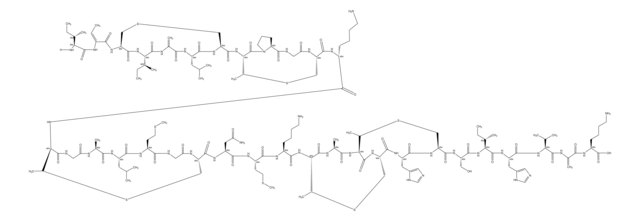
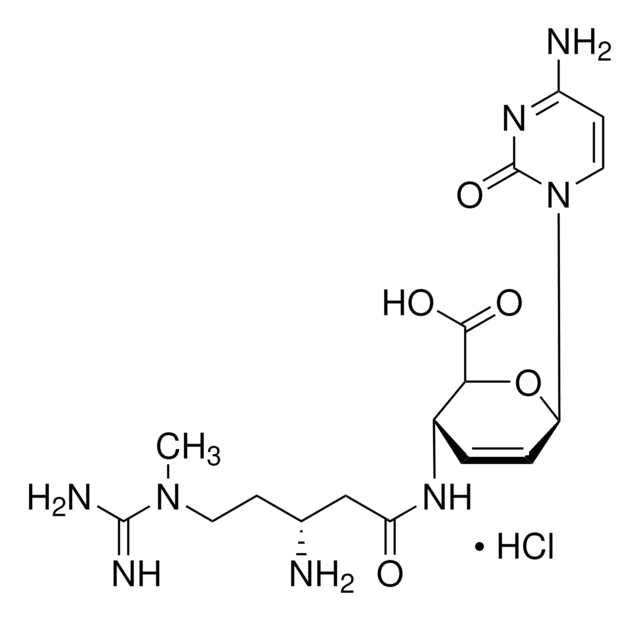
Recommended Products
biological source
Streptomyces noursei
Quality Level
assay
≥85% (HPLC)
form
solid
color
white to light brown
solubility
H2O: soluble 200 mg/mL
suitability
suitable for (selection agent for molecular genetic research work)
antibiotic activity spectrum
Gram-negative bacteria
Gram-positive bacteria
fungi
mycobacteria
mycoplasma
parasites
viruses
yeast
mode of action
protein synthesis | interferes
storage temp.
2-8°C
General description
Chemical structure: peptidyl nucleoside
Application
Noursethricin is used as a dominant selection antibiotic for genetically modified bacteria, yeasts, fungi, protozoa and plants.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Nourseothricin inhibits biosynthesis and induces miscoding. Resistance to nourseothricin is mediated by the sat1 encoded N-acetyltransferase. Nourseothricin is inactivated by acetylation of the β-amino group of the β-lysin.
Antifungal effective against Candida albicans. Candida species transformed with the gene encoding nourseothricin acetyltransferase (CaNAT1) were resistant to nourseothricin.
Packaging
10mg, 100mg
Other Notes
Keep container tightly closed in a dry and well-ventilated place. Store under inert gas.
signalword
Warning
hcodes
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Oral
Storage Class
13 - Non Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Adrian J Verster et al.
G3 (Bethesda, Md.), 7(10), 3337-3347 (2017-08-26)
Genes encoding essential components of core cellular processes are typically highly conserved across eukaryotes. However, a small proportion of essential genes are highly taxonomically restricted; there appear to be no similar genes outside the genomes of highly related species. What
Dorota Fennessy et al.
PloS one, 9(5), e97683-e97683 (2014-05-23)
Targeted alteration of the genome lies at the heart of the exploitation of S. pombe as a model system. The rate of analysis is often determined by the efficiency with which a target locus can be manipulated. For most loci
Kristin L Patrick et al.
Cell systems, 7(3), 323-338 (2018-08-06)
Intracellular bacterial pathogens secrete a repertoire of effector proteins into host cells that are required to hijack cellular pathways and cause disease. Despite decades of research, the molecular functions of most bacterial effectors remain unclear. To address this gap, we
Tomokazu Murakawa et al.
Cell reports, 26(2), 338-345 (2019-01-10)
Degradation of mitochondria by selective autophagy, termed mitophagy, contributes to the control of mitochondrial quality. Bcl2-L-13 is a mammalian homolog of Atg32, which is an essential mitophagy receptor in yeast. However, the molecular machinery involved in Bcl2-L-13-mediated mitophagy remains to
Markus Mund et al.
Cell, 174(4), 884-896 (2018-07-31)
Clathrin-mediated endocytosis is an essential cellular function in all eukaryotes that is driven by a self-assembled macromolecular machine of over 50 different proteins in tens to hundreds of copies. How these proteins are organized to produce endocytic vesicles with high precision
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service