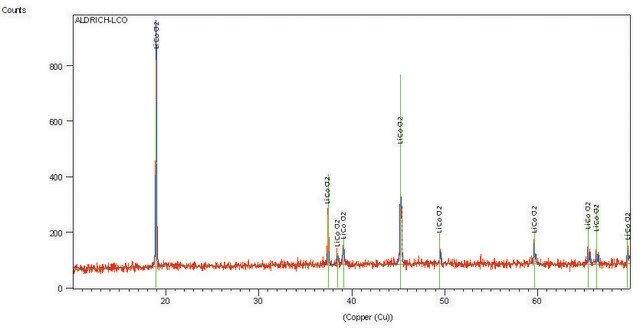
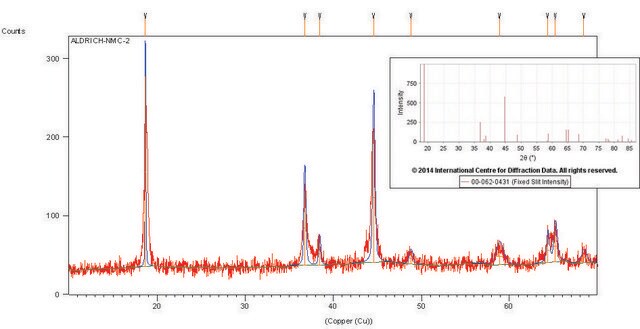
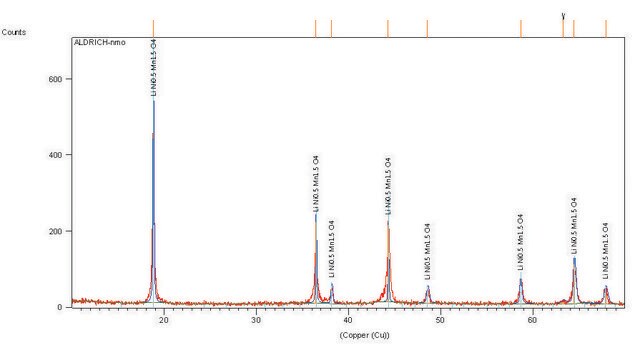
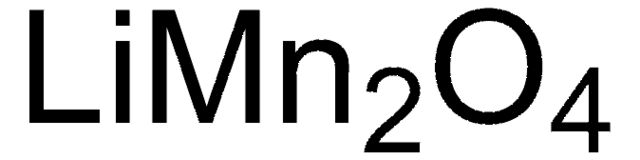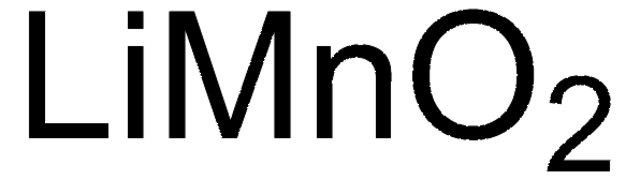757365
Lithium nickel dioxide
powder, <3 μm particle size (BET), ≥98% trace metals basis
Synonym(s):
LNO, Lithium nickel oxide, Lithium nickelate
About This Item
Recommended Products
grade
battery grade
Quality Level
assay
≥98% trace metals basis
form
powder
mol wt
Mw 97.63 g/mol
composition
LiNiO2
particle size
<3 μm (BET)
mp
>1,000 °C (lit.)
density
4.62 g/cm3 (lit.)
application(s)
battery manufacturing
InChI
1S/Li.Ni.2O/q+1;;;-1
InChI key
VROAXDSNYPAOBJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Related Categories
General description
Application
Legal Information
Related product
signalword
Danger
hcodes
Hazard Classifications
Carc. 1A Inhalation - Skin Sens. 1 - STOT RE 1
Storage Class
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Professor Qiao’s laboratory lays out recent advances in conversion type lithium metal fluoride batteries. This review explores key concepts in developing electrochemically stable microstructures for wide Li-ion insertion channels.
Discover more about advancements being made to improve energy density of lithium ion battery materials.
Lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) have been widely adopted as the most promising portable energy source in electronic devices because of their high working voltage, high energy density, and good cyclic performance.
The critical technical challenges associated with the commercialization of electric vehicle batteries include cost, performance, abuse tolerance, and lifespan.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service