Recommended Products
mol wt
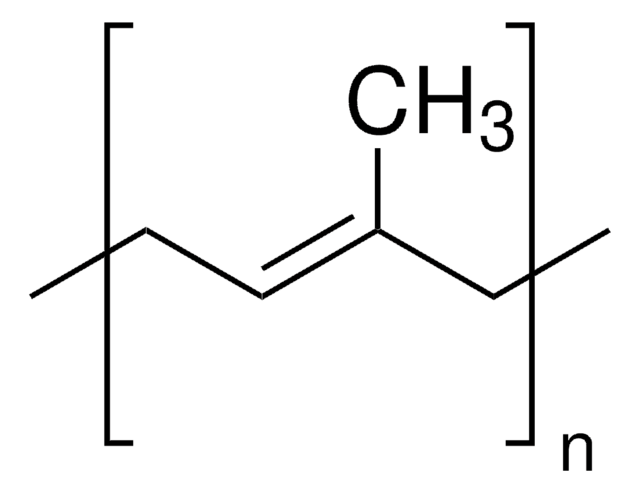
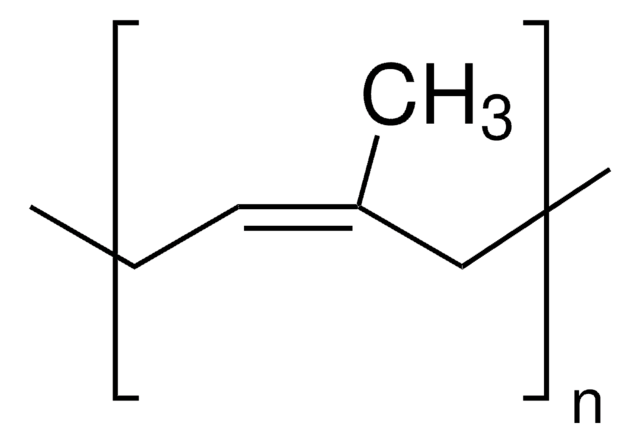
average Mw 60,000-70,000 (polyisoprene)
composition
solids, 27-29 wt. %
dielectric constant
2.4
surface tension
29.2 dyn/cm
viscosity
465-535 cP(25 °C)
bp
122-142 °C (lit.)
density
0.89 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
λmax
310-480 nm
storage temp.
2-8°C
InChI
1S/C14H28O2/c1-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-13-15-11-14(2,3)12-16-13/h13H,4-12H2,1-3H3
InChI key
UBZVSDZJBLSIJG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Related Categories
General description
signalword
Danger
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Inhalation - Aquatic Chronic 3 - Asp. Tox. 1 - Eye Irrit. 2 - Flam. Liq. 3 - Repr. 1B - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
target_organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class
3 - Flammable liquids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
75.2 °F - closed cup
flash_point_c
24 °C - closed cup
ppe
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service