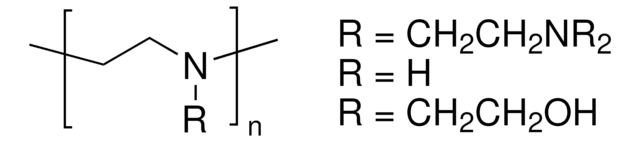408719
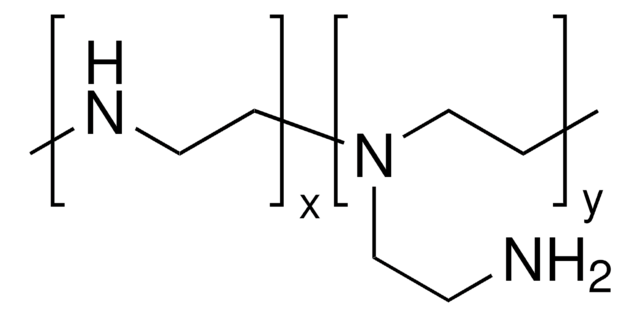
Polyethylenimine, branched
average Mw ~800 by LS, average Mn ~600 by GPC
Synonym(s):
PEI, ethylenediamine branched
About This Item
Recommended Products
form
viscous liquid
Quality Level
mol wt
average Mn ~600 by GPC
average Mw ~800 by LS
refractive index
n20/D 1.5240
density
1.050 g/mL at 25 °C
InChI
1S/C2H8N2.C2H5N/c3-1-2-4;1-2-3-1/h1-4H2;3H,1-2H2
InChI key
SFLOAOINZSFFAE-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Related Categories
General description
Application
Bamboo charcoal impregnated with PEI can be used as a CO2 adsorbent. Numerous amino groups present in PEI can react with CO2 due to acid-alkali interaction and enhance the adsorption capacity of bamboo charcoal.
It can also be used to prepare cross-linked water-soluble polymers with high coordination capabilities towards organic drug molecules.
Features and Benefits
- Branched PEI has better complexation and buffering capacity.
- High ion exchange capacity and affinity toward proteins.
- SignificantDNA transfer efficiency.
Physical form
signalword
Danger
hcodes
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Chronic 2 - Eye Dam. 1
Storage Class
10 - Combustible liquids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
356.0 °F
flash_point_c
180 °C
ppe
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Professor Yoshiki Katayama (Kyushu University, Japan) discusses recent advances in drug delivery systems and strategies that exploit the EPR effect, with a special focus on stimuli-responsive systems based on novel materials.
Gene therapy has become one of the most discussed techniques in biomedical research in recent years.
The CRISPR/Cas9 system has recently emerged as a highly specific, efficient, and versatile gene editing technology that can be utilized to build disease models and correct diseased genes. Safe and effective delivery vectors for the CRISPR/Cas9 system are in critical need to enable clinical development and future applications of CRISPR/Cas9 systems. Professor Yang Liu summarizes recent progress in nonviral nanoparticle approaches for CRISPR/Cas9 delivery.
We present an article that discusses two applications in particular; first, using these layers as polyelectrolyte membranes to control permeability.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service