Kluczowe dokumenty
YEAST1
Yeast Transformation Kit
reagents for introducing plasmid DNA into yeast
Synonim(y):
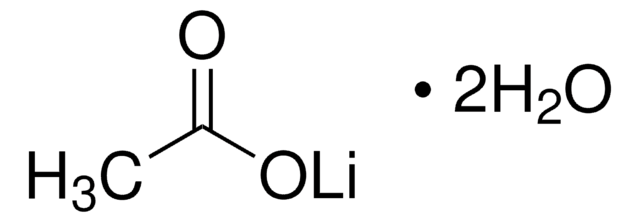
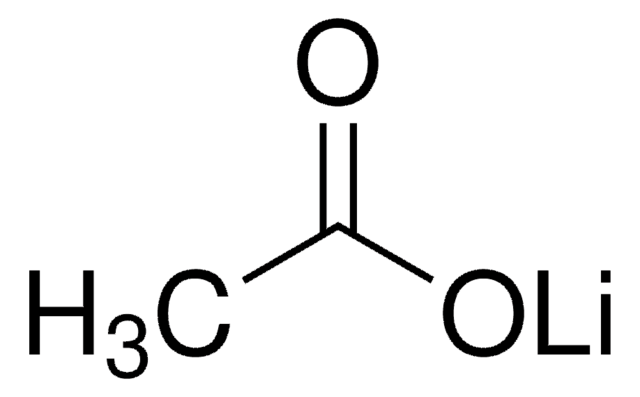
transformacja drożdży octanem litu
About This Item
Polecane produkty
klasa czystości
Molecular Biology
for molecular biology
Poziom jakości
zastosowanie
kit sufficient for >100 standard transformations
metody
transformation: suitable
Warunki transportu
dry ice
temp. przechowywania
−20°C
Powiązane kategorie
Opis ogólny
Zastosowanie
Cechy i korzyści
- Easy and ready-to-use
- Requires as little as 10 ng of plasmid DNA
- Flexibility for any strain of yeast
- Sufficient for over 100 standard transformations
Komponenty
- Transformation Buffer; 100 ml; 100 mM lithium acetate, 10 mM Tris HCl, pH 7.6, and 1 mM EDTA
- Plate Buffer; 100 ml; 40% PEG, 100 mM lithium acetate, 10 mM Tris HCl, pH 7.5, 1 mM EDTA
- Deoxyribonucleic acid from salmon teste, 10 mg/ml; 2 x 1 ml
- Control Yeast Plasmid DNA pRS316 carrying the ura gene; 10 μg
- Yeast Synthetic Drop-out Medium Supplement Without Uracil; 1 g
Zasada
produkt powiązany
Kod klasy składowania
10 - Combustible liquids
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Produkty
Transformation is the process by which exogenous DNA is introduced into a cell, resulting in a heritable change or genetic modification. This was first reported in Streptococcus pneumoniae by Griffith in 1928. Transforming principle of DNA was demonstrated by Avery et al. in 1944.
The development of genetic engineering and cloning has opened many possibilities of expression and isolation of heterologous proteins for research purposes. Considerable advances in technology have enabled expression and isolation of recombinant proteins in large scale.
Inżynieria genetyczna umożliwia ekspresję na dużą skalę i izolację rekombinowanych białek do celów badawczych.
Protokoły
The selection of plasmids in yeast is based on the use of auxotrophic mutant strains, which cannot grow without a specific medium component (an amino acid, purine, or pyrimidine)
Yeasts are considered model systems for eukaryotic studies as they exhibit fast growth and have dispersed cells.
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej