SRP2089
C-myc, proto oncogene human
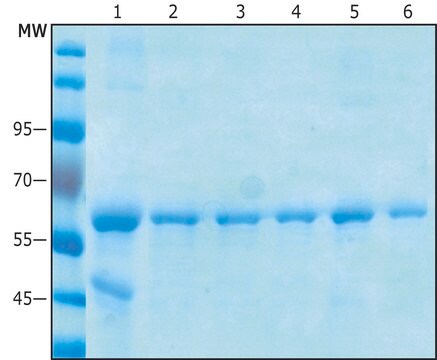
recombinant, expressed in E. coli, ≥80% (SDS-PAGE)
Synonim(y):
MRTL, bHLHe39, c-Myc
About This Item
Polecane produkty
pochodzenie biologiczne
human
rekombinowane
expressed in E. coli
Próba
≥80% (SDS-PAGE)
Postać
frozen liquid
masa cząsteczkowa
~50.4 kDa
opakowanie
pkg of 5 μg
warunki przechowywania
avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles
stężenie
500 μg/mL
kolor
clear
colorless
numer dostępu NCBI
numer dostępu UniProt
Warunki transportu
dry ice
temp. przechowywania
−70°C
informacje o genach
human ... MYC(4609)
Opis ogólny
Działania biochem./fizjol.
Postać fizyczna
Uwaga dotycząca przygotowania
Kod klasy składowania
10 - Combustible liquids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 1
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Certyfikaty analizy (CoA)
Poszukaj Certyfikaty analizy (CoA), wpisując numer partii/serii produktów. Numery serii i partii można znaleźć na etykiecie produktu po słowach „seria” lub „partia”.
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Produkty
We present an article about how proliferating cells require the biosynthesis of structural components for biomass production and for genomic replication.
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej