Wszystkie zdjęcia(1)
Kluczowe dokumenty
SHPH15
MISSION® LentiPlex® Human Pooled shRNA Library TRC1.5
For Rapid, Convenient Genome-wide shRNA Screens
Zaloguj sięWyświetlanie cen organizacyjnych i kontraktowych
About This Item
Kod UNSPSC:
41105904
NACRES:
NA.51
Polecane produkty
Poziom jakości
linia produktu
MISSION®
stężenie
≥5x108 VP/ml (via p24 assay)
metody
capture ELISA: 5 x 108 TU/mL using p24
Warunki transportu
dry ice
temp. przechowywania
−70°C
Powiązane kategorie
Opis ogólny
MISSION LentiPlex Pooled Libraries bring the power of the MISSION TRC shRNA collection together with Sigma′s lentiviral manufacturing expertise to enable genome-wide RNAi screens at your bench-top. The LentiPlex pooled system provides enhanced delivery and long-term gene silencing in non-dividing and primary cell lines allowing unlimited discovery potential. The convenient format now makes rapid whole-genome RNAi screens accessible to any researcher with minimal reagent, time or capital equipment investment.
The MISSION LentiPlex Human shRNA Pooled Library 1.5 includes additional gene and clone coverage from the previously offered LentiPlex 1.0 Pooled Library . With the addition of 1.5, which consists of 4,000+ human genes and 10,000+ total clone coverage divided into 3 subpools, the complete whole-genome human library complete whole-genome human librarynow consists of over 110,000 shRNA constructs from the TRC collection targeting 21,000+ human genes. Each library is tested for shRNA representation before product release to ensure robust library coverage. The complete library is provided in ready-to-use lentiviral format at titers of at least 5 x 108 TU/ml via p24 assay and is pre-divided into sixteen subpools of approximately 6,000-8,000 shRNA constructs each. Amplification and sequencing primers are also provided for downstream target identification.
For more information including sample data and uses, please visit our LentiPlex Technical Detail Page.
The MISSION LentiPlex Human shRNA Pooled Library 1.5 includes additional gene and clone coverage from the previously offered LentiPlex 1.0 Pooled Library . With the addition of 1.5, which consists of 4,000+ human genes and 10,000+ total clone coverage divided into 3 subpools, the complete whole-genome human library complete whole-genome human librarynow consists of over 110,000 shRNA constructs from the TRC collection targeting 21,000+ human genes. Each library is tested for shRNA representation before product release to ensure robust library coverage. The complete library is provided in ready-to-use lentiviral format at titers of at least 5 x 108 TU/ml via p24 assay and is pre-divided into sixteen subpools of approximately 6,000-8,000 shRNA constructs each. Amplification and sequencing primers are also provided for downstream target identification.
For more information including sample data and uses, please visit our LentiPlex Technical Detail Page.
Inne uwagi
The MISSION LentiPlex Human Pooled shRNA Libraries consist of Catalog Numbers SHPH01, SHPH15, SHPH2, and SHPHLIBR. Please refer to Table 1 for approximate number of shRNA clone coverage, targeted genes, and subpools for each library.
Amplification and sequencing primers are also provided for downstream hit identification.
Deconvolution of shRNA Pools
Sigma′s deconvolution service lets you easily identify the genes that impact your pooled shRNA screen.
Contact your local Sigma sales representative for more information or submit an inquiry to MISSION RNAi
Amplification and sequencing primers are also provided for downstream hit identification.
Deconvolution of shRNA Pools
Sigma′s deconvolution service lets you easily identify the genes that impact your pooled shRNA screen.
- Next-generation sequencing of clonesgives a precise number of individual clone occurrence within a pooled shRNA sample
- Comprehensive, reproducible results from pooled shRNA screens
- Statistically robust and information-rich data
Contact your local Sigma sales representative for more information or submit an inquiry to MISSION RNAi
Polecane produkty
Browse additional MISSION shRNA Gene Family Sets in our MISSION shRNA portal.
Informacje prawne
LentiPlex is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
MISSION is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
Ta strona może zawierać tekst przetłumaczony maszynowo.
Kod klasy składowania
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 3
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Certyfikaty analizy (CoA)
Poszukaj Certyfikaty analizy (CoA), wpisując numer partii/serii produktów. Numery serii i partii można znaleźć na etykiecie produktu po słowach „seria” lub „partia”.
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Christine Karlsson et al.
Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, N.J.), 650, 29-43 (2010-08-06)
Identifying the genes and pathways that regulate self-renewal and differentiation in somatic stem cells is a central goal in stem cell and cancer biology. Here, we describe a method for RNAi-based screens in primary human hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells.
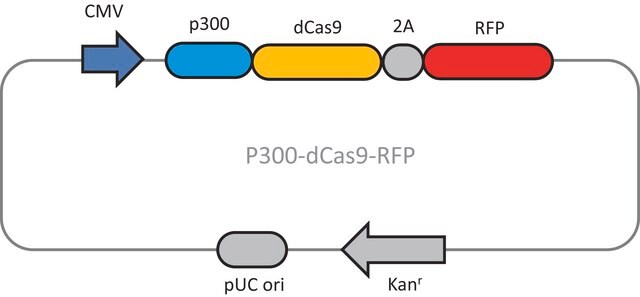
Functional dissection of lysine deacetylases reveals that HDAC1 and p300 regulate AMPK.
Lin, Yu-yi, et al.
Nature (2012)
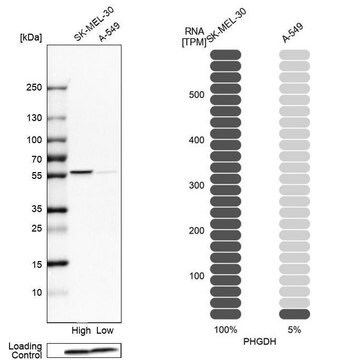
Richard Possemato et al.
Nature, 476(7360), 346-350 (2011-07-16)
Cancer cells adapt their metabolic processes to drive macromolecular biosynthesis for rapid cell growth and proliferation. RNA interference (RNAi)-based loss-of-function screening has proven powerful for the identification of new and interesting cancer targets, and recent studies have used this technology
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej