Wszystkie zdjęcia(2)
Kluczowe dokumenty
MSP02
Membrane Scaffold Protein 1D1 D73C
recombinant, expressed in E. coli, Cysteine substituted at position 73
Zaloguj sięWyświetlanie cen organizacyjnych i kontraktowych
About This Item
Kod UNSPSC:
12352200
NACRES:
NA.26
Polecane produkty
rekombinowane
expressed in E. coli
Poziom jakości
Próba
≥90% (SDS-GE)
Postać
buffered aqueous solution
Warunki transportu
ambient
temp. przechowywania
−20°C
Opis ogólny
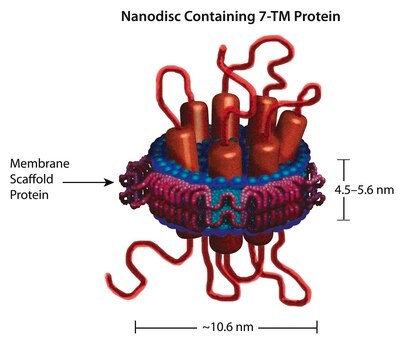
Nanodisc technology is an approach to render membrane proteins soluble in aqueous solutions in a native-like bilayer environment, where the membrane proteins remain stable and active. The Nanodisc concept is derived from high density lipoprotein (HDL) particles and their primary protein component, apolipoprotein. The Nanodisc is a non-covalent structure of phospholipid bilayer and membrane scaffold protein (MSP), a genetically engineered protein, which mimics the function of Apolipoprotein A-1 (ApoA-1).
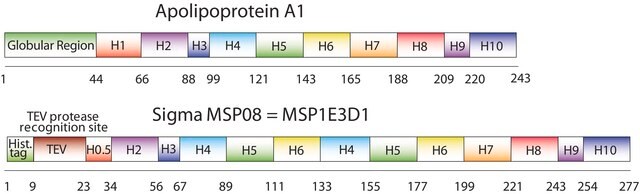
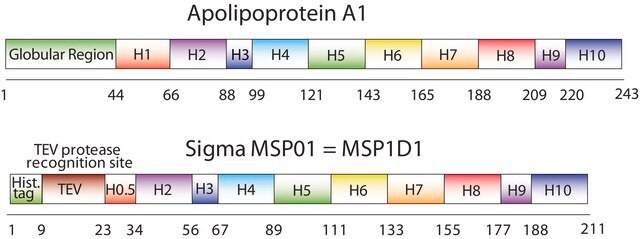
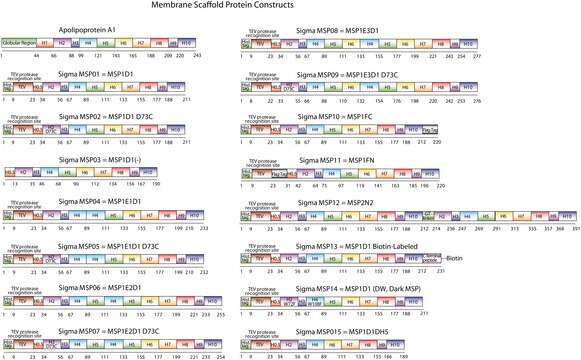
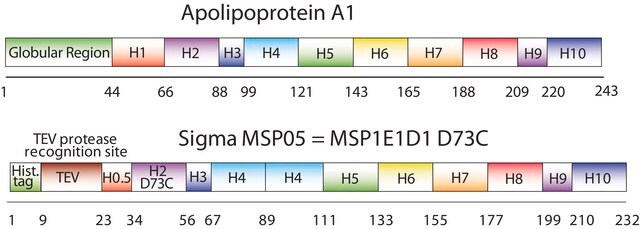
The first MSP, MSP1, was engineered with its sequence based on the sequence of A-1, but without the globular N-terminal domain of native A-1. The Membrane Scaffold Protein 1D1 (MSP1D1) variant of MSP1 deletes the first 11 amino acids in the Helix 1 portion (referred to as “H0.5” in the accompanying figure) of the original MSP1 sequence. The D73C variant of MSP1D1 (MSP1D1 D73C) substitutes a cysteine (C) for an aspartic acid (D) at position 73 of the original native A-1 sequence, within the Helix 2 segment (H2) of the protein.
The first MSP, MSP1, was engineered with its sequence based on the sequence of A-1, but without the globular N-terminal domain of native A-1. The Membrane Scaffold Protein 1D1 (MSP1D1) variant of MSP1 deletes the first 11 amino acids in the Helix 1 portion (referred to as “H0.5” in the accompanying figure) of the original MSP1 sequence. The D73C variant of MSP1D1 (MSP1D1 D73C) substitutes a cysteine (C) for an aspartic acid (D) at position 73 of the original native A-1 sequence, within the Helix 2 segment (H2) of the protein.
Zastosowanie
For guidelines on the use of this and other MSP′s to prepare Nanodiscs, please visit our Protocols for Membrane Scaffold Proteins and Nanodisc Formation page.
Informacje prawne
Nanodisc technology, and many of its uses, are covered by the following patents held by the University of Illinois.
- 7,691,414 Membrane scaffold proteins
- 7,662,410 Membrane scaffold proteins and embedded membrane proteins
- 7,622,437 Tissue factor compositions and methods
- 7,592,008 Membrane scaffold proteins
- 7,575,763 Membrane scaffold proteins and tethered membrane proteins
- 7,083,958 Membrane scaffold proteins
- 7,048,949 Membrane scaffold proteins
Ta strona może zawierać tekst przetłumaczony maszynowo.
Kod klasy składowania
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 2
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Certyfikaty analizy (CoA)
Poszukaj Certyfikaty analizy (CoA), wpisując numer partii/serii produktów. Numery serii i partii można znaleźć na etykiecie produktu po słowach „seria” lub „partia”.
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Protokoły
Protocols for Membrane Scaffold Proteins and Nanodisc Formation
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej