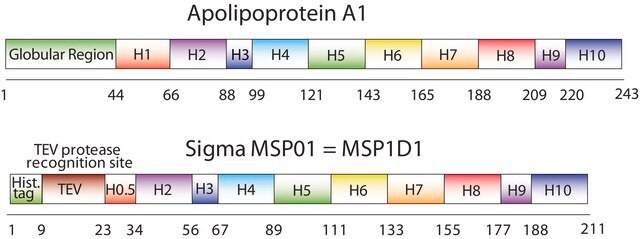
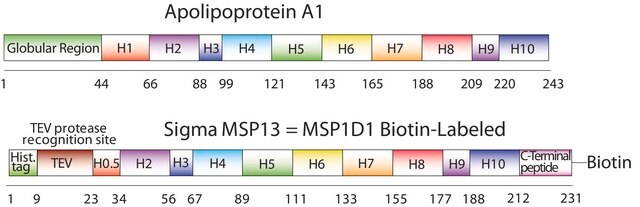
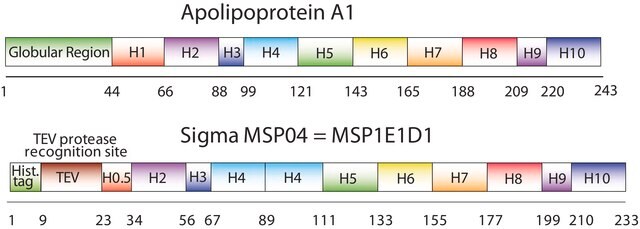
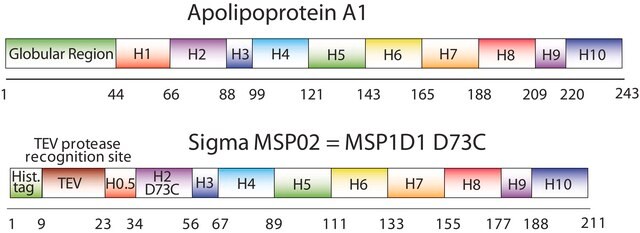
Kluczowe dokumenty
M7074
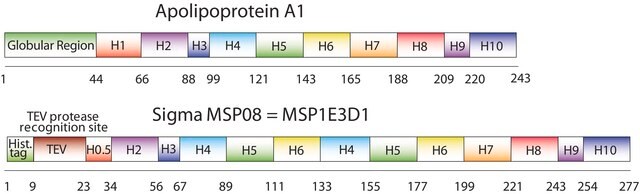
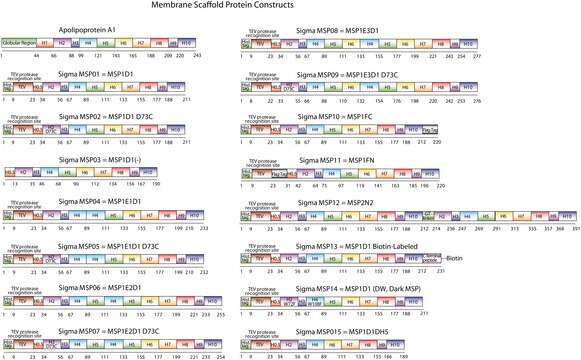
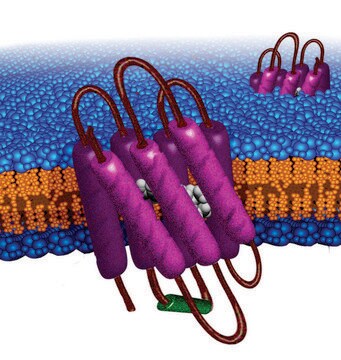
Membrane Scaffold Protein 1E3D1
recombinant, expressed in E. coli
Synonim(y):
MSP1E3D1
About This Item
Polecane produkty
pochodzenie biologiczne
Streptomyces kanamyceticus
Poziom jakości
rekombinowane
expressed in E. coli
opis
N-Terminal histidine-tagged
Formularz
lyophilized powder
masa cząsteczkowa
Mw 32599.98 by amino acid sequence
ε (współczynnik ekstynkcji)
26,600 M-1cm-1 at 280 nm (His-tag-cleaved dissolved in 20 mM Tris pH 7.4, 0.1M NaCl, 0.5mM EDTA and 0.01%NaN3)(lit.)
29,400 M-1cm-1 at 280 nm (uncleaved His-tagged dissolved in 20 mM Tris pH 7.4, 0.1M NaCl, 0.5mM EDTA and 0.01%NaN3)(lit.)
temp. przechowywania
−20°C
Szukasz podobnych produktów? Odwiedź Przewodnik dotyczący porównywania produktów
Opis ogólny
Zastosowanie
Działania biochem./fizjol.
Właściwości fizyczne
Postać fizyczna
Informacje prawne
- 7,691,414 Membrane scaffold proteins
- 7,662,410 Membrane scaffold proteins and embedded membrane proteins
- 7,622,437 Tissue factor compositions and methods
- 7,592,008 Membrane scaffold proteins
- 7,575,763 Membrane scaffold proteins and tethered membrane proteins
- 7,083,958 Membrane scaffold proteins
- 7,048,949 Membrane scaffold proteins
produkt powiązany
Hasło ostrzegawcze
Warning
Zwroty wskazujące rodzaj zagrożenia
Zwroty wskazujące środki ostrożności
Klasyfikacja zagrożeń
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Organy docelowe
Respiratory system
Kod klasy składowania
11 - Combustible Solids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 3
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Produkty
Read our article about how the Nanodisc system allows for structural studies of membrane proteins.
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej