I3036
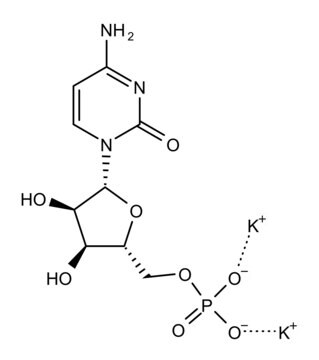
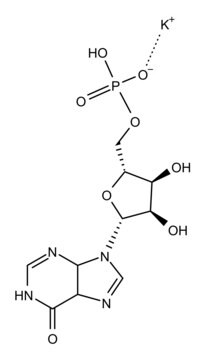
Polyinosinic–polycytidylic acid potassium salt
γ-irradiated
Synonim(y):
Poly (I:C), Poly(I) • Poly(C)
Zaloguj sięWyświetlanie cen organizacyjnych i kontraktowych
About This Item
Polecane produkty
Szukasz podobnych produktów? Odwiedź Przewodnik dotyczący porównywania produktów
Działania biochem./fizjol.
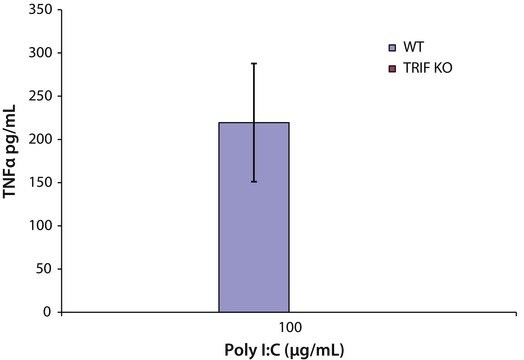
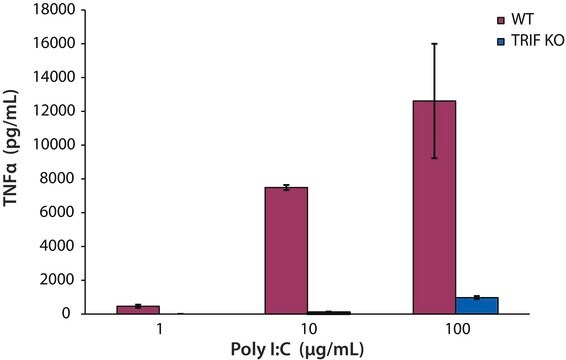
Transfection of Poly (I:C) into NIT-1 cells has been used as a model of intracellular dsRNA-induced β cell apoptosis. Eighteen hours post transfection, 45% of the cells were apoptotic with an increase in NF-kB, p50/p65 nuclear translocation, and cleavage of caspases 3 and 8, as well as transcriptional induction of caspase 12, Fas, IL-15, and the TNF receptor-associated ligand (TRAIL). It has been suggested that Poly(I:C) is one of the most appropriate generators of stable mature dendritic cells (DC). These mature DC might generate in vivo effective immune responses after injection due to their ability to secrete bioactive IL-12 after CD40 ligation. Poly (I:C) was used as a potent adjuvant to enhance the specific anti-tumor immune responses against a peptide-based vaccine.
Opakowanie
Package size based on polynucleotide content
Inne uwagi
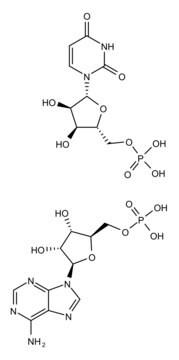
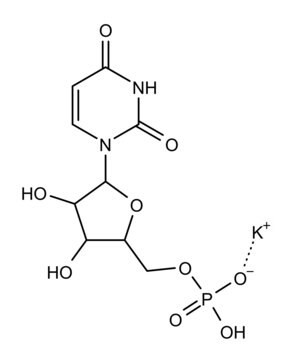
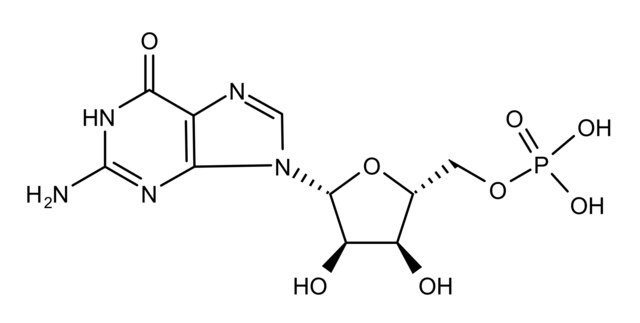
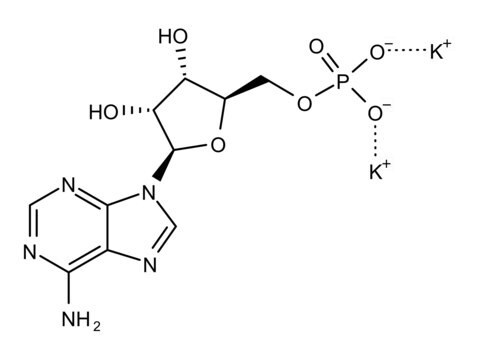
Double-stranded homopolymer.
Postać fizyczna
10% Poly (I:C) with sodium chloride and sodium phosphate buffer salts
Ta strona może zawierać tekst przetłumaczony maszynowo.
Kod klasy składowania
11 - Combustible Solids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 3
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Lingjun Meng et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 112(35), 11007-11012 (2015-08-19)
Systematic inflammation contributes to the development of many diseases, including cardiovascular disease, which is the leading cause of mortality worldwide. How such inflammation is initiated and maintained throughout the course of disease remains unclear. In the current study, we report
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej