Kluczowe dokumenty
C9972
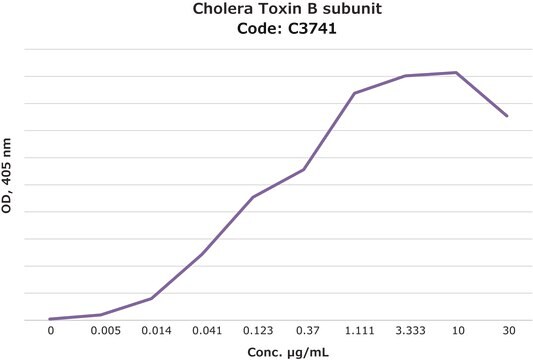
Cholera Toxin B subunit
biotin conjugate, lyophilized powder
Synonim(y):
CTB
About This Item
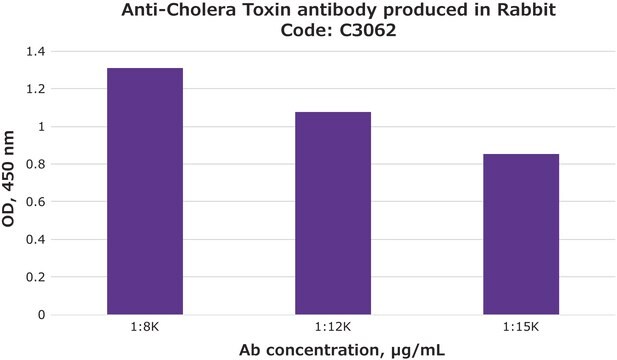
Polecane produkty
białko sprzężone
biotin conjugate
Poziom jakości
Formularz
lyophilized powder
masa cząsteczkowa
~12 kDa
skład
Protein, ~40% Lowry
temp. przechowywania
2-8°C
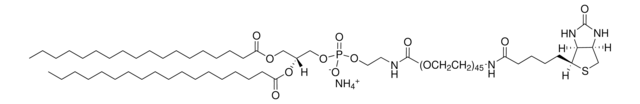
ciąg SMILES
CCOc1ccccc1C(=O)Nc2ccc(Cl)c(c2)C(F)(F)F
InChI
1S/C16H13ClF3NO2/c1-2-23-14-6-4-3-5-11(14)15(22)21-10-7-8-13(17)12(9-10)16(18,19)20/h3-9H,2H2,1H3,(H,21,22)
Klucz InChI
YDXZSNHARVUYNM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Szukasz podobnych produktów? Odwiedź Przewodnik dotyczący porównywania produktów
Opis ogólny
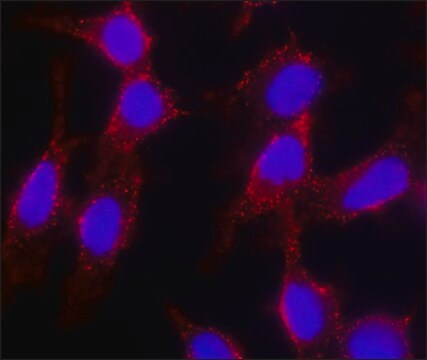
Zastosowanie
- in immunofluorescence
- in the analysis of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II lipid raft partitioning
- in live cell three-dimensional tracking of SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells
- to assess the toll-like receptors (TLR) and FcRγ (Fc receptor γ chain) – CARD9 (caspase recruitment domain family member 9) activation by cholera Toxin B (CTB)
Działania biochem./fizjol.
Jakość
Postać fizyczna
Komentarz do analizy
Zwroty wskazujące rodzaj zagrożenia
Zwroty wskazujące środki ostrożności
Klasyfikacja zagrożeń
Aquatic Chronic 3
Kod klasy składowania
11 - Combustible Solids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 3
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Środki ochrony indywidualnej
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej