Kluczowe dokumenty
C9281
Cholesterol Esterase from Pseudomonas fluorescens
lyophilized powder, ≥10,000 units/g protein
Synonim(y):
CE, bile salt-stimulated lipase, cholesteryl ester hydrolase, pancreatic cholesterol esterase, Sterol-ester acylhydrolase
About This Item
Polecane produkty
pochodzenie biologiczne
Pseudomonas fluorescens
Poziom jakości
Próba
10-30% (TCA-Biuret)
Formularz
lyophilized powder
aktywność właściwa
≥10,000 units/g protein
masa cząsteczkowa
~129 kDa
skład
Protein, ~20%
warunki przechowywania
under inert gas (argon)
metody
cell based assay: suitable
kolor
tan to brown
pH
7-9
rozpuszczalność
0.4 M potassium phosphate, pH 7.0: soluble 1.0 mg/mL
temp. przechowywania
−20°C
Szukasz podobnych produktów? Odwiedź Przewodnik dotyczący porównywania produktów
Opis ogólny
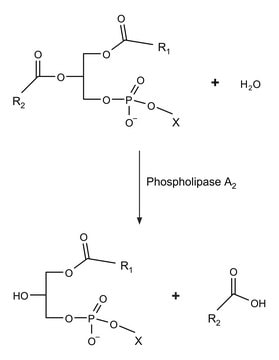
Cholesterol Esterase (CE) is a glycoprotein that can be isolated from fungal species such as Candida cylindracea and Pseudomonas fluorescens. It is classified as a member of the lipase/esterase family and functions as a homo-dimeric protein. CE is produced in the pancreas and is released in an active form upon stimulation by Cholecystokinin (CCK).
Zastosowanie
- in cholesterol esterase assay to quantify total cholesterol from human blood serum samples
- a study to investigate the nondenaturing protein electro transfer of the esterase activity of lipolytic preparations
- an optimization study of components in enzymatic cholesterol reagents containing cholesterol oxidase
- for the modification of human plasma low-density-lipoprotein (LDL) to induce endothelial cell (EC) dysfunction and monocyte (MC) adhesion in the branched tissue-engineered blood vessels (TEBVs)
- to hydrolyze native cholesterol ester (CE) during filipin staining for detection of CE within the retinal frozen sections
Działania biochem./fizjol.
Inne uwagi
Definicja jednostki
Komentarz do analizy
Hasło ostrzegawcze
Danger
Zwroty wskazujące rodzaj zagrożenia
Zwroty wskazujące środki ostrożności
Klasyfikacja zagrożeń
Resp. Sens. 1
Kod klasy składowania
11 - Combustible Solids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 1
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Środki ochrony indywidualnej
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Certyfikaty analizy (CoA)
Nie widzisz odpowiedniej wersji?
Jeśli potrzebujesz konkretnej wersji, możesz wyszukać konkretny certyfikat według numeru partii lub serii.
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Produkty
Cholesterol undergoes esterification to improve transport. Cholesterol esters are more easily packaged into the interior of lipoproteins - increasing the quantity that can be readily transported in the blood stream.
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej