Kluczowe dokumenty
A5512
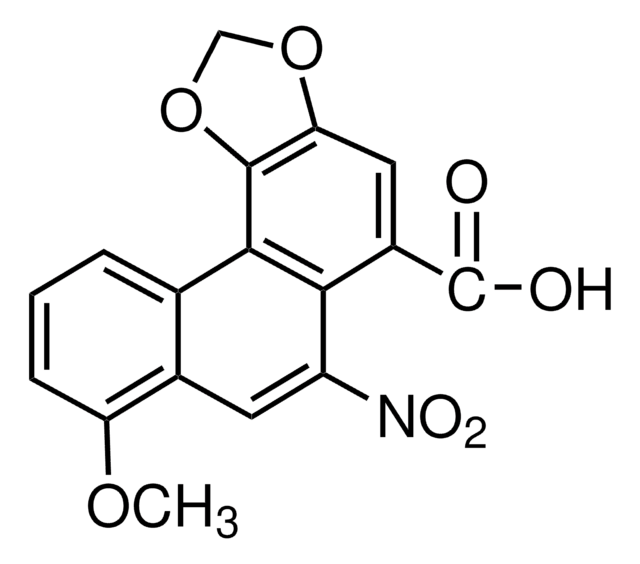
Aristolochic acid I
≥90% (HPLC), powder, phospholipase A₂ inhibitor
Synonim(y):
TR 1736
About This Item
Polecane produkty
Nazwa produktu
Aristolochic acid I, powder
Próba
≥90% (HPLC)
Formularz
powder
kolor
yellow
mp
269-270 °C
rozpuszczalność
DMSO: soluble
ethanol: soluble
temp. przechowywania
2-8°C
ciąg SMILES
COc1cccc2c1cc([N+]([O-])=O)c3c(cc4OCOc4c23)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C17H11NO7/c1-23-12-4-2-3-8-9(12)5-11(18(21)22)14-10(17(19)20)6-13-16(15(8)14)25-7-24-13/h2-6H,7H2,1H3,(H,19,20)
Klucz InChI
BBFQZRXNYIEMAW-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Szukasz podobnych produktów? Odwiedź Przewodnik dotyczący porównywania produktów
Opis ogólny
Zastosowanie
- as a standard for the analysis of Aristolochia sprucei crude extract by high-performance liquid chromatography
- to study its effects on histone deacetylase 3 (HDAC3) aberration and renal fibrosis
- to induce acute aristolochic acid nephropathy and to study its impact on miRNA and mRNA expression in mice
Działania biochem./fizjol.
Hasło ostrzegawcze
Danger
Zwroty wskazujące rodzaj zagrożenia
Zwroty wskazujące środki ostrożności
Klasyfikacja zagrożeń
Acute Tox. 3 Oral - Carc. 1A - Muta. 1B
Kod klasy składowania
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 3
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Środki ochrony indywidualnej
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type P2 (EN 143) respirator cartridges
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Produkty
Carcinogenesis and Epigenetics
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej