Key Documents
11189
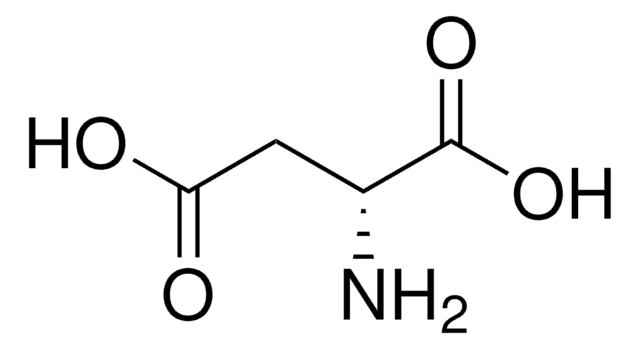
L-Aspartic acid
≥99.5% (T), BioUltra
Synonim(y):
(S)-(+)-Aminosuccinic acid, (S)-Aminobutanedioic acid
About This Item
Polecane produkty
product name
L-Aspartic acid, BioUltra, ≥99.5% (T)
linia produktu
BioUltra
Poziom jakości
Próba
≥99.5% (T)
Postać
powder or crystals
aktywność optyczna
[α]20/D +24.7±1°, c = 5% in 5 M HCl
zanieczyszczenia
insoluble matter, passes filter test
≤0.3% foreign amino acids
pozostałość po prażeniu
≤0.05% (as SO4)
strata
≤0.1% loss on drying, 110 °C
kolor
white
mp
>300 °C (dec.) (lit.)
rozpuszczalność
1 M HCl: 0.5 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless
ślady anionów
chloride (Cl-): ≤50 mg/kg
sulfate (SO42-): ≤150 mg/kg
ślady kationów
Al: ≤5 mg/kg
As: ≤0.1 mg/kg
Ba: ≤5 mg/kg
Bi: ≤5 mg/kg
Ca: ≤10 mg/kg
Cd: ≤5 mg/kg
Co: ≤5 mg/kg
Cr: ≤5 mg/kg
Cu: ≤5 mg/kg
Fe: ≤5 mg/kg
K: ≤50 mg/kg
Li: ≤5 mg/kg
Mg: ≤5 mg/kg
Mn: ≤5 mg/kg
Mo: ≤5 mg/kg
NH4+: ≤200 mg/kg
Na: ≤100 mg/kg
Ni: ≤5 mg/kg
Pb: ≤5 mg/kg
Sr: ≤5 mg/kg
Zn: ≤5 mg/kg
λ
0.5 M in 1 M HCl
absorpcja UV
λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.20
λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.10
ciąg SMILES
N[C@@H](CC(O)=O)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C4H7NO4/c5-2(4(8)9)1-3(6)7/h2H,1,5H2,(H,6,7)(H,8,9)/t2-/m0/s1
Klucz InChI
CKLJMWTZIZZHCS-REOHCLBHSA-N
informacje o genach
human ... CA1(759) , CA2(760)
rat ... Grin2a(24409)
Szukasz podobnych produktów? Odwiedź Przewodnik dotyczący porównywania produktów
Opis ogólny
Zastosowanie
- as a metabolite to study the enzyme–metabolite interactions in the central metabolism of Escherichia coli by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)
- in transmission electron microscopy
- as a component of complete media for culturing Yeast strain
Działania biochem./fizjol.
Kod klasy składowania
11 - Combustible Solids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 1
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Środki ochrony indywidualnej
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Certyfikaty analizy (CoA)
Poszukaj Certyfikaty analizy (CoA), wpisując numer partii/serii produktów. Numery serii i partii można znaleźć na etykiecie produktu po słowach „seria” lub „partia”.
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej