Kluczowe dokumenty
270555
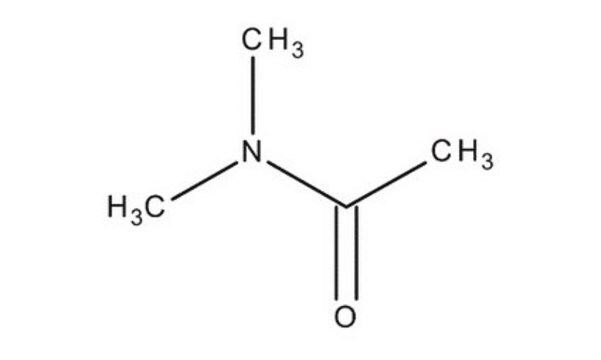
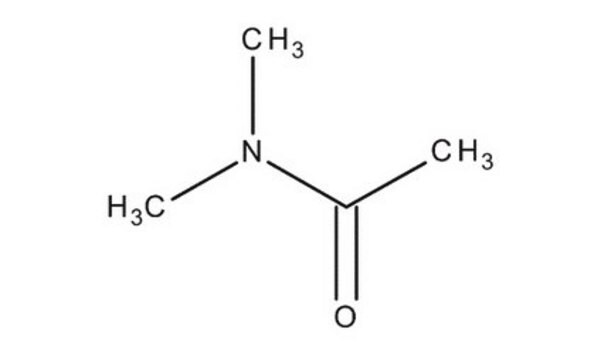
N,N-Dimethylacetamide
suitable for HPLC, ≥99.9%
About This Item
Polecane produkty
klasa czystości
HPLC grade
gęstość pary
3 (vs air)
ciśnienie pary
2 mmHg ( 25 °C)
4 mmHg ( 38 °C)
Próba
≥99.9%
Formularz
liquid
temp. samozapłonu
914 °F
granice wybuchowości
1.8 %, 100 °F
11.5 %, 160 °F
metody
HPLC: suitable
zanieczyszczenia
<0.030% water
pozostałość po odparowaniu
<0.001%
współczynnik refrakcji
n20/D 1.437 (lit.)
pH
4 (20 °C, 200 g/L)
bp
164.5-166 °C (lit.)
mp
−20 °C (lit.)
gęstość
0.937 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
λ
H2O reference
absorpcja UV
λ: 270 nm Amax: 1.00
λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.30
λ: 290 nm Amax: 0.15
λ: 310 nm Amax: 0.05
λ: 320 nm Amax: 0.03
λ: 360-400 nm Amax: 0.01
Zastosowanie
food and beverages
ciąg SMILES
CN(C)C(C)=O
InChI
1S/C4H9NO/c1-4(6)5(2)3/h1-3H3
Klucz InChI
FXHOOIRPVKKKFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Szukasz podobnych produktów? Odwiedź Przewodnik dotyczący porównywania produktów
Powiązane kategorie
Zastosowanie
- Ternary Phase-Field Simulation of Poly(vinylidene fluoride) Microporous Membrane Structures Prepared by Nonsolvent-Induced Phase Separation with Different Additives and Solvent Treatments: Badanie to podkreśla zastosowanie N,N-dimetyloacetamidu (DMAC) w przygotowaniu zaawansowanych membran z poli(fluorku winylidenu), pokazując jego kluczową rolę w ulepszaniu przetwarzania polimerów i struktur membran w materiałoznawstwie (Zhang et al., 2024).
- Ulepszona wydajność usuwania białek przez membranę ultrafiltracyjną PES z pustymi włóknami o strukturze przypominającej gąbkę: Badania wykazały skuteczność DMAC w produkcji wysokowydajnych membran ultrafiltracyjnych, podkreślając jego znaczenie w zastosowaniach biomedycznych i oczyszczaniu ścieków (Zhao et al., 2024).
- Aerożele poli(fluorku winylidenu) z alfa, beta i gamma; Formy krystaliczne: Korelacja właściwości fizykochemicznych ze strukturami polimorficznymi: Artykuł przedstawia wszechstronność DMAC jako rozpuszczalnika w syntezie aerożeli poli(fluorku winylidenu), łącząc jego zastosowanie ze znaczącymi postępami w zrozumieniu krystaliczności i właściwości polimeru (Suresh et al., 2024).
- Estry celulozy: Synteza w celu dalszego tworzenia warstw z nanocząstkami magnetytu: Badanie wykorzystuje DMAC do syntezy zaawansowanych warstw estrów celulozy zintegrowanych z nanocząstkami magnetytu, ilustrując jego potencjał w opracowywaniu wielofunkcyjnych materiałów do różnych zastosowań przemysłowych (Furlan Sandrini et al., 2024).
Opakowanie
Jako światowy lider w dziedzinie odczynników laboratoryjnych nieustannie poszukujemy nowych sposobów optymalizacji bezpieczeństwa naszych produktów. Nowo opracowana konstrukcja butelki na rozpuszczalniki o pojemności 4 l jest wyposażona w zaawansowaną technologię uszczelniania, która eliminuje wycieki, dzięki czemu obsługa rozpuszczalników jest bezpieczniejsza i wygodniejsza niż kiedykolwiek wcześniej.
Zobacz wszystkie nowe funkcje tutaj!
Hasło ostrzegawcze
Danger
Zwroty wskazujące rodzaj zagrożenia
Zwroty wskazujące środki ostrożności
Klasyfikacja zagrożeń
Acute Tox. 4 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Inhalation - Eye Irrit. 2 - Repr. 1B
Kod klasy składowania
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 2
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
147.2 °F - closed cup
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
64 °C - closed cup
Wykazy regulacyjne
Wykazy regulacyjne dotyczą głównie produktów chemicznych. Można w nich podawać ograniczoną liczbę informacji na temat produktów niechemicznych. Brak wpisu oznacza, że żaden ze składników nie znajduje się w wykazie. Użytkownik odpowiada za zagwarantowanie bezpiecznego i zgodnego z prawem stosowania produktu.
EU REACH SVHC Candidate List
EU REACH Annex XVII (Restriction List)
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej