Kluczowe dokumenty
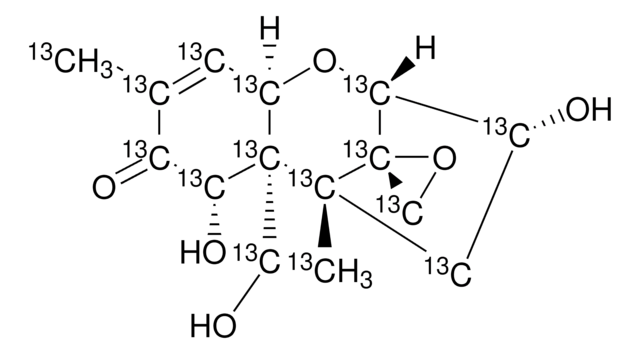
IRMM315
4-Deoxynivalenol in acetonitrile
IRMM®, certified reference material
Synonim(y):
Deoxynivalenol solution, 3α,7α,15-Trihydroxy-12,13-epoxytrichothec-9-en-8-one, DON, Vomitoxin
About This Item
Polecane produkty
klasa czystości
certified reference material
agency
IRMM®
producent / nazwa handlowa
JRC
Zastosowanie
general analytical
Format
matrix material
temp. przechowywania
2-8°C
ciąg SMILES
CC1=C[C@H]2O[C@@H]3[C@H](O)C[C@@](C)([C@]34CO4)[C@@]2(CO)[C@H](O)C1=O
InChI
1S/C15H20O6/c1-7-3-9-14(5-16,11(19)10(7)18)13(2)4-8(17)12(21-9)15(13)6-20-15/h3,8-9,11-12,16-17,19H,4-6H2,1-2H3/t8-,9-,11-,12-,13-,14-,15+/m1/s1
Klucz InChI
LINOMUASTDIRTM-QGRHZQQGSA-N
Szukasz podobnych produktów? Odwiedź Przewodnik dotyczący porównywania produktów
Opis ogólny
Komentarz do analizy
IRMM315
Informacje prawne
Hasło ostrzegawcze
Danger
Zwroty wskazujące rodzaj zagrożenia
Zwroty wskazujące środki ostrożności
Klasyfikacja zagrożeń
Acute Tox. 4 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Irrit. 2 - Flam. Liq. 2
Kod klasy składowania
3 - Flammable liquids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 2
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
35.6 °F - closed cup
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
2.0 °C - closed cup
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Certyfikaty analizy (CoA)
Przepraszamy, ale COA dla tego produktu nie jest aktualnie dostępny online.
Proszę o kontakt, jeśli potrzebna jest pomoc Obsługa Klienta
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej