8.00762
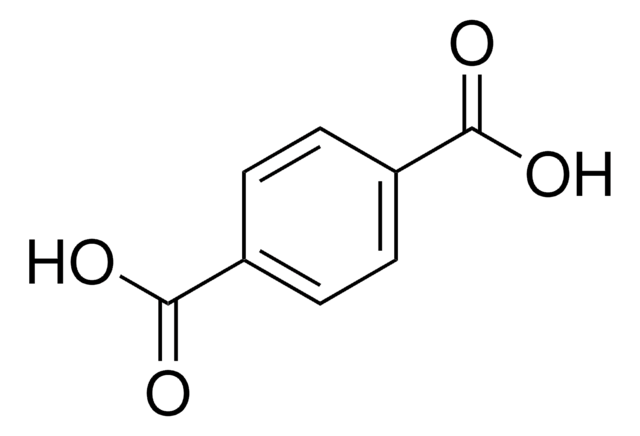
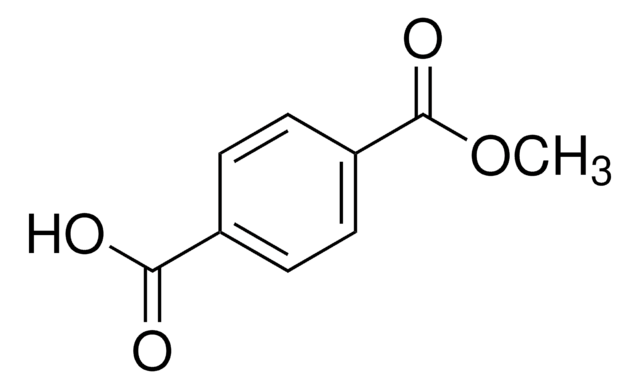
Kwas tereftalowy
for synthesis
Synonim(y):
Terephthalic acid, 1,4-Benzenedicarboxylic acid, p-Phthalic acid
About This Item
Polecane produkty
klasa czystości
for synthesis
synthesis grade
Poziom jakości
Próba
≥98% (acidimetric)
Formularz
crystalline
temp. samozapłonu
496 °C
siła działania
>6400 mg/kg LD50, oral (Rat)
mp
402 °C (sublimed)
rozpuszczalność
15 mg/L (experimental)
gęstość
1.51 g/cm3 at 20 °C
temp. przechowywania
2-30°C
ciąg SMILES
[O-]C(=O)c1ccc(cc1)C(=O)[O-].[H+].[H+]
InChI
1S/C8H6O4/c9-7(10)5-1-2-6(4-3-5)8(11)12/h1-4H,(H,9,10)(H,11,12)
Klucz InChI
KKEYFWRCBNTPAC-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Zastosowanie
- Biotransformacja p-ksylenu do kwasu tereftalowego przez zmodyfikowane genetycznie bakterie Escherichia coli: W niniejszym badaniu zbadano alternatywną metodę produkcji kwasu tereftalowego (TPA), która może być mniej energochłonna i bezpieczniejsza niż tradycyjne metody. Opisuje ono udaną biokonwersję p-ksylenu do TPA przy użyciu genetycznie zmodyfikowanych bakterii E. coli, podkreślając potencjalne zrównoważone podejście do produkcji TPA (Luo & Lee, 2017).
- Synteza i weryfikacja biopochodnego kwasu tereftalowego z furfuralu: Badania te przedstawiają nową syntetyczną ścieżkę produkcji TPA z furfuralu pochodzącego z biomasy. Stanowi to znaczący krok w kierunku zrównoważonej produkcji chemicznej, zapewniając bardziej ekologiczną alternatywę dla szlaków petrochemicznych (Tachibana, Kimura & Kasuya, 2015).
- Badania nad rozpuszczalnością kwasu tereftalowego w cieczach jonowych: Skupiając się na identyfikacji lepszych rozpuszczalników dla TPA, w niniejszym badaniu zbadano rozpuszczalność TPA w różnych cieczach jonowych. Odkrycia mogą prowadzić do ulepszonych technik przetwarzania TPA w zastosowaniach przemysłowych (Matuszek et al., 2019).
- Inżynieryjny produkt kwasu tereftalowego z recyklingu butelek PET: W tym badaniu zbadano depolimeryzację PET do TPA i glikolu etylenowego, podkreślając zrównoważone podejście do recyklingu odpadów PET i zmniejszenia zależności od produktów petrochemicznych (Lee, Chiu & Lee, 2021).
- Biopochodne technologie kwasu tereftalowego - przegląd literatury: Przegląd różnych biopochodnych podejść do produkcji TPA, koncentrując się na potencjale odnawialnych surowców do zastąpienia tradycyjnych szlaków petrochemicznych. Ten kompleksowy przegląd omawia różne biotechnologiczne i chemiczne metody syntezy TPA ze źródeł biologicznych (Collias et al., 2014).
Komentarz do analizy
Identity (IR): passes test
Kod klasy składowania
11 - Combustible Solids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 1
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Certyfikaty analizy (CoA)
Poszukaj Certyfikaty analizy (CoA), wpisując numer partii/serii produktów. Numery serii i partii można znaleźć na etykiecie produktu po słowach „seria” lub „partia”.
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej