1.00489
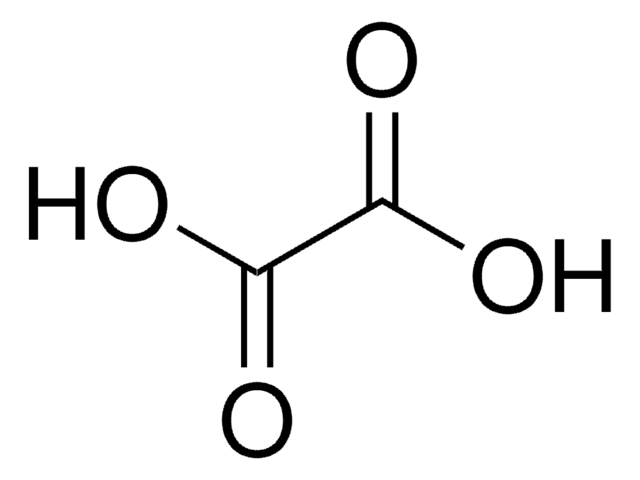
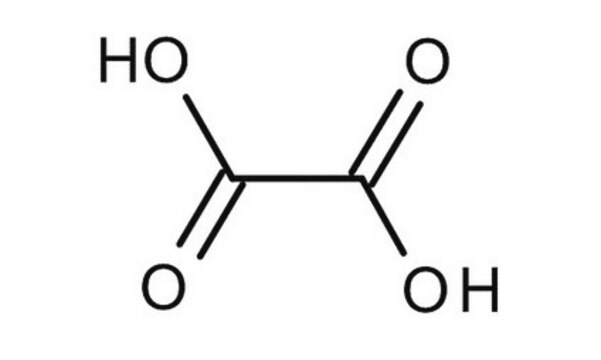
Oxalic acid dihydrate
Suprapur®
Synonim(y):
Oxalic acid dihydrate, Ethanedioic acid
About This Item
Polecane produkty
klasa czystości
for inorganic trace analysis
Poziom jakości
ciśnienie pary
0.000312 hPa ( 25 °C)
Próba
≥99.5% (calculated as dihydrate, alkalimetric)
Postać
solid
siła działania
375 mg/kg LD50, oral (Rat)
pH
1.5 (10 g/L in H2O)
tw
149-160 °C/1013 hPa (decomposition)
mp
98-100 °C
temp. przejścia
flash point 157 °C (decomposition)
rozpuszczalność
water: >100 g/L at 25 °C
gęstość
1.65 g/cm3 at 20 °C
gęstość nasypowa
813 kg/m3
ślady anionów
chloride (Cl-): ≤5000 ppb
phosphate (PO43-): ≤500 ppb
sulfate (SO42-): ≤2000 ppb
ślady kationów
Ag: ≤10 ppb
Al: ≤20 ppb
As: ≤1.0 ppb
Au: ≤1.0 ppb
Ba: ≤100 ppb
Be: ≤1.0 ppb
Bi: ≤1.0 ppb
Ca: ≤100 ppb
Cd: ≤50 ppb
Co: ≤5 ppb
Cr: ≤10 ppb
Cu: ≤5 ppb
Fe: ≤50 ppb
Ga: ≤1.0 ppb
Ge: ≤1.0 ppb
In: ≤1.0 ppb
K: ≤200 ppb
Li: ≤5 ppb
Mg: ≤20 ppb
Mn: ≤5 ppb
Mo: ≤5 ppb
Na: ≤100 ppb
Ni: ≤10 ppb
Pb: ≤10 ppb
Pt: ≤1.0 ppb
Sb: ≤1.0 ppb
Sn: ≤5 ppb
Sr: ≤100 ppb
Ti: ≤5 ppb
Tl: ≤1.0 ppb
U: ≤1.0 ppb
V: ≤10 ppb
Zn: ≤20 ppb
temp. przechowywania
2-30°C
InChI
1S/C2H2O4.2H2O/c3-1(4)2(5)6;;/h(H,3,4)(H,5,6);2*1H2
Klucz InChI
GEVPUGOOGXGPIO-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Zastosowanie
- Reaction Atmosphere-Controlled Thermal Conversion of Ferrocene to Hematite and Cementite Nanomaterials-Structural and Spectroscopic Investigations.: This study investigates the conversion of ferrocene to hematite and cementite nanomaterials under controlled thermal conditions. The structural and spectroscopic properties of the resulting materials were analyzed, providing insights into their potential applications in various fields of chemistry and materials science (Kundu et al., 2024).
- Insights into a Co-precursor Driven Solid-State Thermal Reaction of Ferrocene Carboxaldehyde Leading to Hematite Nanomaterial: A Reaction Kinetic Study.: This research focuses on the solid-state thermal reaction of ferrocene carboxaldehyde with oxalic acid dihydrate, leading to hematite nanomaterial. The study provides detailed reaction kinetics and potential applications in catalysis and materials science (Chakraborty et al., 2023).
- Supramolecular Structure of Microwave Treated Bamboo for Production of Lignin-Containing Nanocellulose by Oxalic Acid Dihydrate.: The paper explores the use of oxalic acid dihydrate in the microwave treatment of bamboo to produce lignin-containing nanocellulose. This process enhances the material properties of nanocellulose, offering applications in sustainable materials and bioengineering (Wang et al., 2023).
- Thermo-Mechano-Chemical Deconstruction of Cellulose for Cellulose Nanocrystal Production by Reactive Processing.: This study presents a method for producing cellulose nanocrystals using thermo-mechano-chemical deconstruction with oxalic acid dihydrate. The resulting nanocrystals have potential uses in biocomposites and nanomaterials (Guiao et al., 2022).
- Formation and Structure Evolution of Starch Nanoplatelets by Deep Eutectic Solvent of Choline Chloride/Oxalic Acid Dihydrate Treatment.: This research investigates the formation of starch nanoplatelets using a deep eutectic solvent comprising choline chloride and oxalic acid dihydrate. The study highlights the structural evolution and potential applications in food science and materials engineering (Xiao et al., 2022).
Komentarz do analizy
Chloride (Cl): ≤ 5000 ppb
Phosphate (PO₄): ≤ 500 ppb
Sulfate (SO₄): ≤ 2000 ppb
Ag (Silver): ≤ 10 ppb
Al (Aluminium): ≤ 20 ppb
As (Arsenic): ≤ 1.0 ppb
Au (Gold): ≤ 1.0 ppb
Ba (Barium): ≤ 100 ppb
Be (Beryllium): ≤ 1.0 ppb
Bi (Bismuth): ≤ 1.0 ppb
Ca (Calcium): ≤ 100 ppb
Cd (Cadmium): ≤ 50 ppb
Co (Cobalt): ≤ 5 ppb
Cr (Chromium): ≤ 10 ppb
Cu (Copper): ≤ 5 ppb
Fe (Iron): ≤ 50 ppb
Ga (Gallium): ≤ 1.0 ppb
Ge (Germanium): ≤ 1.0 ppb
In (Indium): ≤ 1.0 ppb
K (Potassium): ≤ 200 ppb
Li (Lithium): ≤ 5 ppb
Mg (Magnesium): ≤ 20 ppb
Mn (Manganese): ≤ 5 ppb
Mo (Molybdenum): ≤ 5 ppb
Na (Sodium): ≤ 100 ppb
Ni (Nickel): ≤ 10 ppb
Pb (Lead): ≤ 10 ppb
Pt (Platinum): ≤ 1.0 ppb
Sb (Antimony): ≤ 1.0 ppb
Sn (Tin): ≤ 5 ppb
Sr (Strontium): ≤ 100 ppb
Ti (Titanium): ≤ 5 ppb
Tl (Thallium): ≤ 1.0 ppb
U (Uranium): ≤ 1.0 ppb
V (Vanadium): ≤ 10 ppb
Zn (Zinc): ≤ 20 ppb
Informacje prawne
Hasło ostrzegawcze
Danger
Zwroty wskazujące rodzaj zagrożenia
Zwroty wskazujące środki ostrożności
Klasyfikacja zagrożeń
Acute Tox. 4 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Dam. 1
Kod klasy składowania
11 - Combustible Solids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 1
Certyfikaty analizy (CoA)
Poszukaj Certyfikaty analizy (CoA), wpisując numer partii/serii produktów. Numery serii i partii można znaleźć na etykiecie produktu po słowach „seria” lub „partia”.
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej