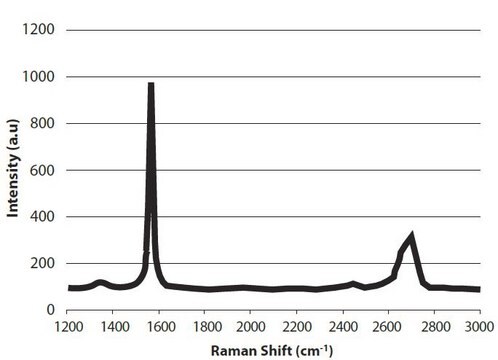
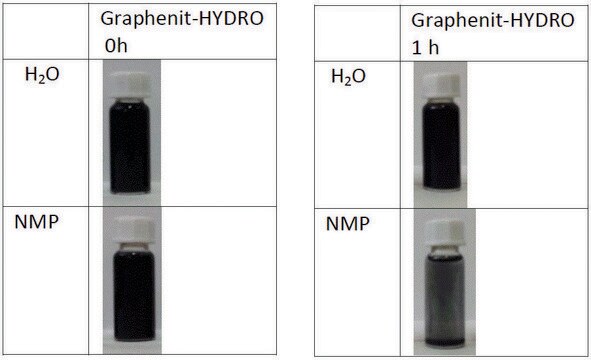
806668
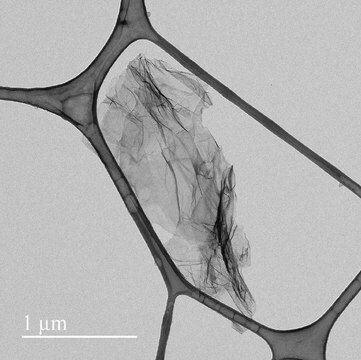
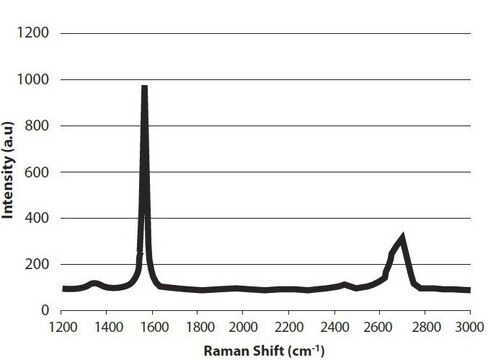
Graphene nanoplatelets
powder, hydrophobic
About This Item
Polecane produkty
Postać
powder
skład
Carbon, >95 wt. %
Oxygen, <2 wt. %
gęstość nasypowa
0.04 g/mL
Szukasz podobnych produktów? Odwiedź Przewodnik dotyczący porównywania produktów
Opis ogólny
Zastosowanie
- Graphene (nano)composite materials
- Conductive coatings
- Anti-corrosion coatings
- Conductive Inks
- Energy Storage
- Electrode materials
Hasło ostrzegawcze
Warning
Zwroty wskazujące rodzaj zagrożenia
Zwroty wskazujące środki ostrożności
Klasyfikacja zagrożeń
Eye Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Organy docelowe
Respiratory system
Kod klasy składowania
11 - Combustible Solids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 3
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Certyfikaty analizy (CoA)
Nie widzisz odpowiedniej wersji?
Jeśli potrzebujesz konkretnej wersji, możesz wyszukać konkretny certyfikat według numeru partii lub serii.
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Produkty
Since its discovery little more than a decade ago,1 the two-dimensional (2D) allotrope of carbon—graphene—has been the subject of intense multidisciplinary research efforts.
Advanced technologies for energy conversion and storage are widely sought after for their potential to improve consumer and electronic device performance as well as for the prospect of reducing the societal and environmental impact of energy generation.
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej