Kluczowe dokumenty
529265
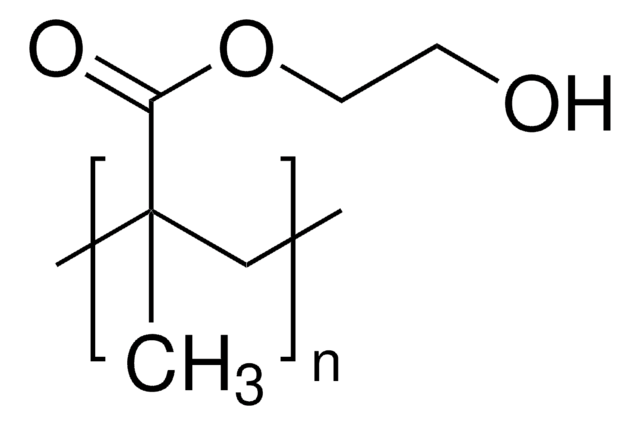
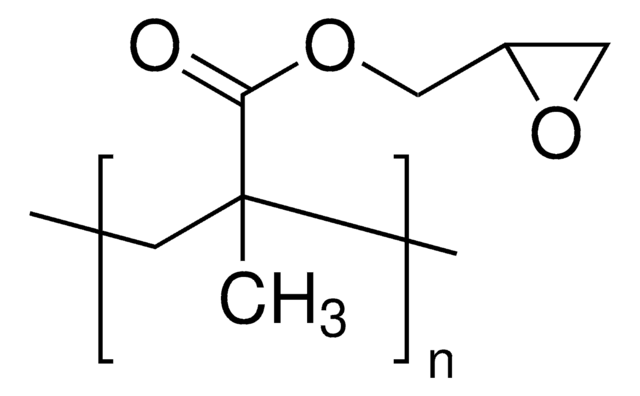
Poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate)
average Mv 20,000
Synonim(y):
Poly(2-HEMA), Poly-HEMA
About This Item
Polecane produkty
Formularz
powder
masa cząsteczkowa
average Mv 20,000
temp. przejścia
Tg 84.8 °C
gęstość
1.15 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
ciąg SMILES
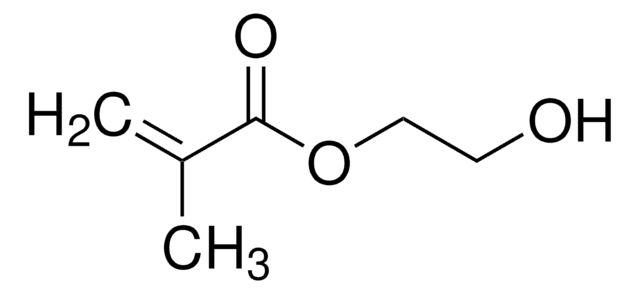
CC(=C)C(=O)OCCO
InChI
1S/C6H10O3/c1-5(2)6(8)9-4-3-7/h7H,1,3-4H2,2H3
Klucz InChI
WOBHKFSMXKNTIM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Szukasz podobnych produktów? Odwiedź Przewodnik dotyczący porównywania produktów
Zastosowanie
- Hydrogen-bonds structure in poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) studied by temperature-dependent infrared spectroscopy: Investigates the hydrogen-bond structure in poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) (PHEMA) using temperature-dependent IR spectroscopy. (S Morita, 2014).
- Transparent and tough poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) hydrogels prepared in water/IL mixtures: Describes the development of tough and transparent PHEMA hydrogels for potential use in various biomedical applications. (Y Liu et al., 2020).
- Reduced cell attachment to poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate)-coated ventricular catheters in vitro: Examines how PHEMA coatings can reduce cell attachment, which is beneficial for biomedical devices like catheters. (BW Hanak et al., 2018).
- Surface modification of poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) hydrogel for contact lens application: Studies modifications to PHEMA hydrogels to improve their suitability for contact lens applications. (M Kazemi Ashtiani, M Zandi, 2018).
Postać fizyczna
Kod klasy składowania
11 - Combustible Solids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 3
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Środki ochrony indywidualnej
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Produkty
Profesor Shrike Zhang (Harvard Medical School, USA) omawia postępy w biodruku 3D modeli tkankowych do testowania leków in vitro, dokonuje przeglądu wyboru biokomponentów i przedstawia przykłady zastosowań biodruku 3D w biofabrykacji modeli tkankowych.
Professor Shrike Zhang (Harvard Medical School, USA) discusses advances in 3D-bioprinted tissue models for in vitro drug testing, reviews bioink selections, and provides application examples of 3D bioprinting in tissue model biofabrication.
Professor Shrike Zhang (Harvard Medical School, USA) discusses advances in 3D-bioprinted tissue models for in vitro drug testing, reviews bioink selections, and provides application examples of 3D bioprinting in tissue model biofabrication.
Self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) have attracted enormous interest for a wide variety of applications in micro- and nano-technology. In this article, we compare the benefits of three different classes of SAM systems (alkylthiolates on gold.
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej