Kluczowe dokumenty
102601
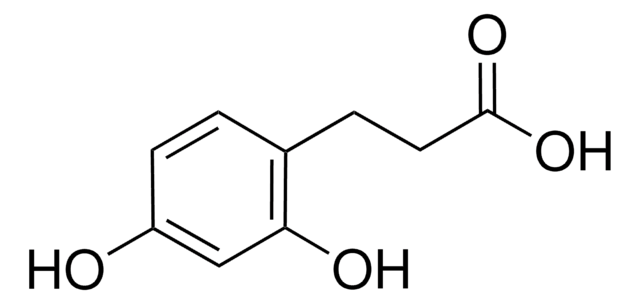
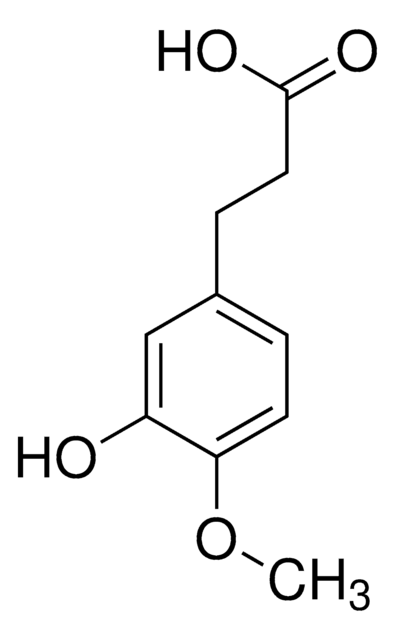
3,4-Dihydroxyhydrocinnamic acid
98%
Synonim(y):
3-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)propionic acid, Hydrocaffeic acid
About This Item
Polecane produkty
Próba
98%
mp
136-139 °C (lit.)
ciąg SMILES
OC(=O)CCc1ccc(O)c(O)c1
InChI
1S/C9H10O4/c10-7-3-1-6(5-8(7)11)2-4-9(12)13/h1,3,5,10-11H,2,4H2,(H,12,13)
Klucz InChI
DZAUWHJDUNRCTF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Szukasz podobnych produktów? Odwiedź Przewodnik dotyczący porównywania produktów
Powiązane kategorie
Opis ogólny
Zastosowanie
It can also be used for thesurface functionalization of nanoparticles. The functionalization with DHCA notonly improves the water solubility of nanoparticles but also provides a platformfor further modification due to the presence of surface carboxyl groups.
Hasło ostrzegawcze
Warning
Zwroty wskazujące rodzaj zagrożenia
Zwroty wskazujące środki ostrożności
Klasyfikacja zagrożeń
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Organy docelowe
Respiratory system
Kod klasy składowania
11 - Combustible Solids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 3
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Środki ochrony indywidualnej
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej