추천 제품
설명
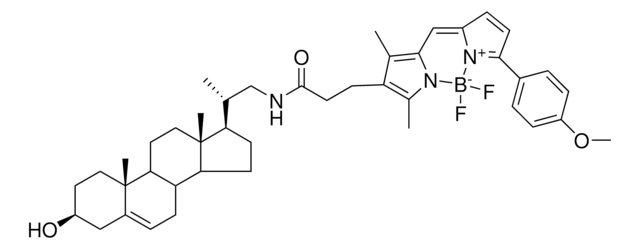
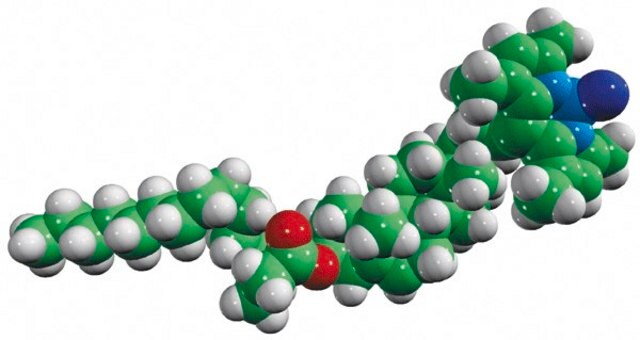
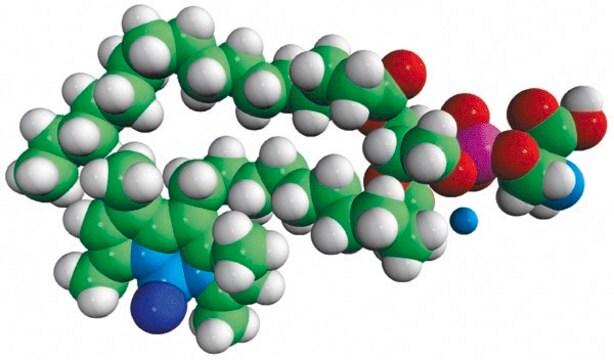
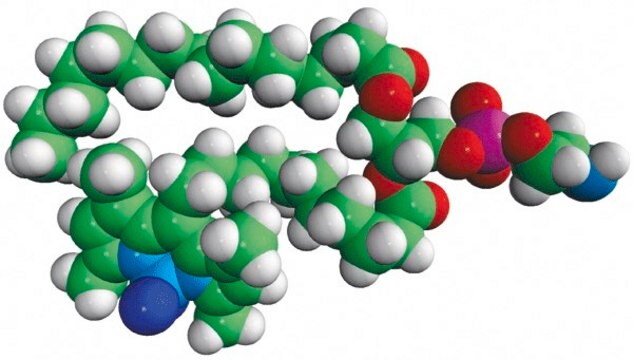
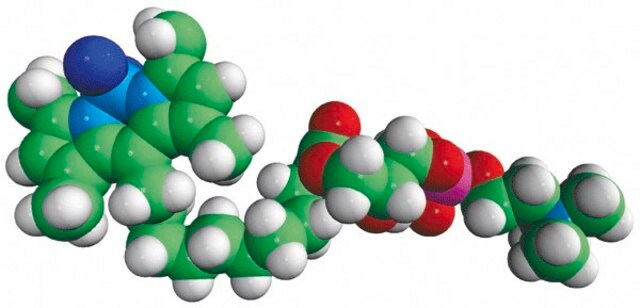
23-(dipyrrometheneboron difluoride)-24-norcholesterol
분석
>99% (TLC)
양식
powder
포장
pkg of 1 × 1 mg (810255P-1mg)
pkg of 1 × 10 mg (810255P-10mg)
pkg of 1 × 5 mg (810255P-5mg)
제조업체/상표
Avanti Research™ - A Croda Brand
배송 상태
dry ice
저장 온도
−20°C
일반 설명
Biomolecules attached to BODIPY, is readily absorbed in the visible light. It results in greater fluorescence quantum yields. It is highly photostable and less sensitive to change in polarity and pH.
애플리케이션
TOPFLUOR™Cholesterol is suitable:
- for cholesterol-uptake assay
- for BODIPY cholesterol labeling in live cell experiments
- for the formation of giant Janus liposomes via poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA)-assisted lipid swelling
생화학적/생리학적 작용
BODIPY labelled cholesterol has similar properties to that of the naïve cholesterol. This serves as a cholesterol marker for live cells and aids in trafficking intracellular cholesterol. It might also help in indicating lipid storage diseases.
포장
5 mL Amber Glass Screw Cap Vial (810255P-10mg)
5 mL Amber Glass Screw Cap Vial (810255P-1mg)
5 mL Amber Glass Screw Cap Vial (810255P-5mg)
법적 정보
Avanti Research is a trademark of Avanti Polar Lipids, LLC
TopFluor is a trademark of Avanti Polar Lipids, LLC
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
가장 최신 버전 중 하나를 선택하세요:
이미 열람한 고객
Frederik W Lund et al.
BMC biophysics, 5, 20-20 (2012-10-20)
Cholesterol is an important membrane component, but our knowledge about its transport in cells is sparse. Previous imaging studies using dehydroergosterol (DHE), an intrinsically fluorescent sterol from yeast, have established that vesicular and non-vesicular transport modes contribute to sterol trafficking
Maarit Hölttä-Vuori et al.
Traffic (Copenhagen, Denmark), 9(11), 1839-1849 (2008-07-24)
Analysis of sterol distribution and transport in living cells has been hampered by the lack of bright, photostable fluorescent sterol derivatives that closely resemble cholesterol. In this study, we employed atomistic simulations and experiments to characterize a cholesterol compound with
Florly S Ariola et al.
Biophysical journal, 96(7), 2696-2708 (2009-04-08)
Cholesterol-rich, liquid-ordered (L(o)) domains are believed to be biologically relevant, and yet detailed knowledge about them, especially in live cells under physiological conditions, is elusive. Although these domains have been observed in model membranes, understanding cholesterol-lipid interactions at the molecular
James E Shaw et al.
Journal of structural biology, 155(3), 458-469 (2006-08-08)
Elucidating the role that charged membrane proteins play in determining cell membrane structure and dynamics is an area of active study. We have applied in situ correlated atomic force and confocal microscopies to characterize the interaction of the NAP-22 peptide
Sandhya Sankaranarayanan et al.
Journal of lipid research, 52(12), 2332-2340 (2011-10-01)
Studies have shown a negative association between cellular cholesterol efflux and coronary artery disease (CAD). Standard protocol for quantitating cholesterol efflux involves labeling cells with [(3)H]cholesterol and measuring release of the labeled sterol. Using [(3)H]cholesterol is not ideal for the
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.