おすすめの製品
品質水準
アッセイ
≥98% (HPLC)
フォーム
powder
色
white to beige
溶解性
DMSO: 2 mg/mL, clear (warmed)
保管温度
2-8°C
SMILES記法
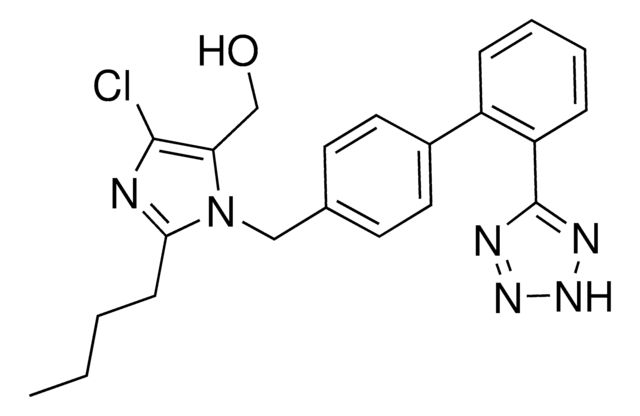
OC1=CC=C(C=C1)CC(N)(C(O)=O)CF
InChI
1S/C10H12FNO3/c11-6-10(12,9(14)15)5-7-1-3-8(13)4-2-7/h1-4,13H,5-6,12H2,(H,14,15)
InChI Key
ACIQAJKTARSFHQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
関連するカテゴリー
生物化学的/生理学的作用
A racemic mixture of D- and L-AFMT. L-AFMT is reported to selectively inhibt against gut bacteria E. faecalis pyridoxal-5′-phosphate (PLP)-dependent tyrosine decarboxylase (TyrDC)-, but not aromatic amino acid decarboxylase (AADC)-, mediated L-dopa decarboxylation (IC50 = 4.7 μM/cell-free, 1.4 μM/in E. faecalis cultures; 20% human AADC inhibition at 650 μM) via covalent adduct formation with TyrDC co-factor PLP. When co-administered with L-dopa (10 mg/kg) and the AADC inhibitor carbidopa (30 mg/kg) to gnotobiotic mice colonized with E. faecalis, L-AFMT (25 mg/kg) significantly increases L-dopa peak serum concentration.
Covalent inhibtor against L-dopa decarboxylation by gut bacteria E. faecalis tyrosine decarboxylase (TyrDC), but not aromatic amino acid decarboxylase (AADC).
保管分類コード
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
引火点(°F)
Not applicable
引火点(℃)
Not applicable
適用法令
試験研究用途を考慮した関連法令を主に挙げております。化学物質以外については、一部の情報のみ提供しています。 製品を安全かつ合法的に使用することは、使用者の義務です。最新情報により修正される場合があります。WEBの反映には時間を要することがあるため、適宜SDSをご参照ください。
Jan Code
SML3100-5MG:
SML3100-VAR:
SML3100-BULK:
SML3100-25MG:
最新バージョンのいずれかを選択してください:
Vayu Maini Rekdal et al.
Science (New York, N.Y.), 364(6445) (2019-06-15)
The human gut microbiota metabolizes the Parkinson's disease medication Levodopa (l-dopa), potentially reducing drug availability and causing side effects. However, the organisms, genes, and enzymes responsible for this activity in patients and their susceptibility to inhibition by host-targeted drugs are
ライフサイエンス、有機合成、材料科学、クロマトグラフィー、分析など、あらゆる分野の研究に経験のあるメンバーがおります。.
製品に関するお問い合わせはこちら(テクニカルサービス)