おすすめの製品
製品種目
MISSION®
濃度
≥1x106 VP/ml (via p24 assay)
テクニック
capture ELISA: 106 TU/mL using p24
輸送温度
dry ice
保管温度
−70°C
類似した製品をお探しですか? 訪問 製品比較ガイド
詳細
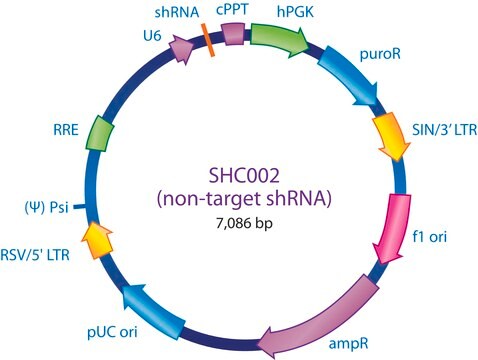
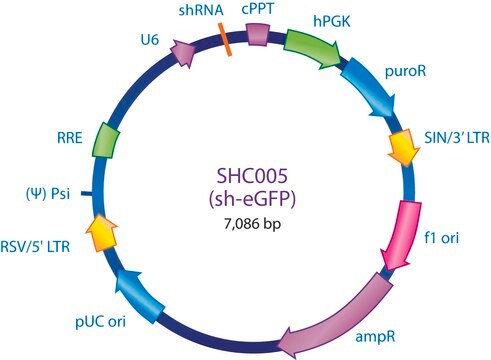
MISSION eGFP shRNAコントロールトランスダクション粒子にはeGFP(GenBank Accession No. pEGFP U55761)を標的とするshRNA配列が含まれています。eGFP shRNAコントロール粒子は、eGFPを発現する細胞株を使用した実験でノックダウンのポジティブコントロールとして有効です。
eGFP shRNAコントロールトランスダクション粒子は、既知配列のレンチウイルスプラスミドpLKO.1-puro-eGFP shRNA(製品番号SHC005)から作製されています。適合するパッケージングプラスミドと同時トランスフェクションすることにより、パッケージング細胞中(HEK293T)に自己不活性化した複製能力のないウイルス粒子が作製されます。さらに、コントロールトランスダクション粒子は水泡性口内炎ウイルスエンベロープG糖タンパク質(VSV-G)でシュードタイピングされていることから、様々な哺乳動物細胞の形質導入が可能です。106 TU/mL(p24力価測定)のレンチウイルス粒子を200 μLの凍結ストック液としてご提供しています。
eGFP shRNAコントロールトランスダクション粒子は、既知配列のレンチウイルスプラスミドpLKO.1-puro-eGFP shRNA(製品番号SHC005)から作製されています。適合するパッケージングプラスミドと同時トランスフェクションすることにより、パッケージング細胞中(HEK293T)に自己不活性化した複製能力のないウイルス粒子が作製されます。さらに、コントロールトランスダクション粒子は水泡性口内炎ウイルスエンベロープG糖タンパク質(VSV-G)でシュードタイピングされていることから、様々な哺乳動物細胞の形質導入が可能です。106 TU/mL(p24力価測定)のレンチウイルス粒子を200 μLの凍結ストック液としてご提供しています。
MISSION® shRNAクローンを用いた実験を行う際には、ノックダウン結果を正確に解釈するために、実験計画において適切なコントロールを選択することが重要です。The MISSION Control Transduction Particleは、トランスダクション効率をモニターするための重要なポジティブコントロールです。
アプリケーションデータ、プロトコール、ベクターマップの詳細は、sigma.com/shrnaをご覧ください。
アプリケーションデータ、プロトコール、ベクターマップの詳細は、sigma.com/shrnaをご覧ください。
アプリケーション
アプリケーションデータ、プロトコール、ベクターマップの詳細は、sigma.com/shrnaをご覧ください。
法的情報
MISSION is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
推奨
製品番号
詳細
価格
保管分類コード
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
WGK 3
引火点(°F)
Not applicable
引火点(℃)
Not applicable
個人用保護具 (PPE)
Eyeshields, Gloves, multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US)
適用法令
試験研究用途を考慮した関連法令を主に挙げております。化学物質以外については、一部の情報のみ提供しています。 製品を安全かつ合法的に使用することは、使用者の義務です。最新情報により修正される場合があります。WEBの反映には時間を要することがあるため、適宜SDSをご参照ください。
カルタヘナ法
カルタヘナ法
試験成績書(COA)
製品のロット番号・バッチ番号を入力して、試験成績書(COA) を検索できます。ロット番号・バッチ番号は、製品ラベルに「Lot」または「Batch」に続いて記載されています。
この製品を見ている人はこちらもチェック
The SCN9A channel and plasma membrane depolarization promote cellular senescence through Rb pathway.
Marine Warnier et al.
Aging cell, 17(3), e12736-e12736 (2018-02-16)
Oncogenic signals lead to premature senescence in normal human cells causing a proliferation arrest and the elimination of these defective cells by immune cells. Oncogene-induced senescence (OIS) prevents aberrant cell division and tumor initiation. In order to identify new regulators
Mariano J Alvarez et al.
Nature genetics, 50(7), 979-989 (2018-06-20)
We introduce and validate a new precision oncology framework for the systematic prioritization of drugs targeting mechanistic tumor dependencies in individual patients. Compounds are prioritized on the basis of their ability to invert the concerted activity of master regulator proteins
R Zufferey et al.
Journal of virology, 72(12), 9873-9880 (1998-11-13)
In vivo transduction of nondividing cells by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1)-based vectors results in transgene expression that is stable over several months. However, the use of HIV-1 vectors raises concerns about their safety. Here we describe a self-inactivating
Cell-cycle dependent expression of a translocation-mediated fusion oncogene mediates checkpoint adaptation in rhabdomyosarcoma.
Kikuchi K, Hettmer S, Aslam MI, et al.
PLoS Genetics, 10(1), e1004107-e1004107 (2014)
Ruth S Cruz Cosme et al.
Journal of virology, 83(7), 2839-2850 (2009-01-16)
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV), a member of the beta subgroup of the family Herpesviridae, causes serious health problems worldwide. HCMV gene expression in host cells is a well-defined sequential process: immediate-early (IE) gene expression, early-gene expression, DNA replication, and late-gene expression.
ライフサイエンス、有機合成、材料科学、クロマトグラフィー、分析など、あらゆる分野の研究に経験のあるメンバーがおります。.
製品に関するお問い合わせはこちら(テクニカルサービス)