すべての画像(1)
About This Item
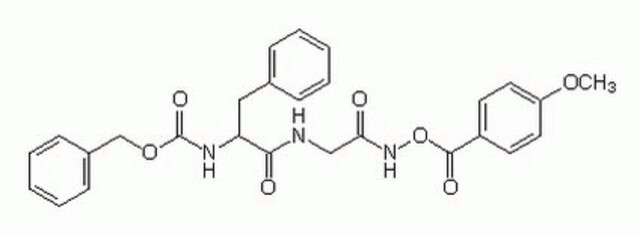
化学式:
C21H23N2O4F
分子量:
386.42
MDL番号:
UNSPSCコード:
12352209
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.77
おすすめの製品
品質水準
アッセイ
≥90% (TLC)
形状
powder
色
white to off-white
溶解性
DMSO or DMF: 20 mM
輸送温度
dry ice
保管温度
−20°C
SMILES記法
C[C@H](NC(=O)[C@H](Cc1ccccc1)NC(=O)OCc2ccccc2)C(=O)CF
InChI
1S/C21H23FN2O4/c1-15(19(25)13-22)23-20(26)18(12-16-8-4-2-5-9-16)24-21(27)28-14-17-10-6-3-7-11-17/h2-11,15,18H,12-14H2,1H3,(H,23,26)(H,24,27)/t15-,18-/m0/s1
InChI Key
ASXVEBPEZMSPHB-YJBOKZPZSA-N
アプリケーション
Z-Phe-Ala fluoromethyl ketone (Z-FA-FMK) has been used as a:
- cathepsin inhibitor to study its effects on dendritic cells
- papain-like cysteine protease inhibitor to study its effects on cadmium-induced mitochondrial apoptosis
- cysteine protease inhibitor to study its effects on the interaction of toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9) with granulin in RAW macrophages
生物化学的/生理学的作用
Z-Phe-Ala fluoromethyl ketone (Z-FA-FMK) is an inhibitor of cysteine proteases, such as cathepsin B and L. It can also inhibit recombinant effector caspases 2, -3, -6, and -7 and not initiator caspases 8 and -10. Z-FA-FMK plays a role in blocking nuclear factor κ-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) transactivation. It exhibits therapeutic effects against rheumatoid arthritis.
保管分類コード
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
引火点(°F)
Not applicable
引火点(℃)
Not applicable
個人用保護具 (PPE)
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
適用法令
試験研究用途を考慮した関連法令を主に挙げております。化学物質以外については、一部の情報のみ提供しています。 製品を安全かつ合法的に使用することは、使用者の義務です。最新情報により修正される場合があります。WEBの反映には時間を要することがあるため、適宜SDSをご参照ください。
Jan Code
C1480-BULK:
C1480-3MG:
C1480-3MG-PW:
C1480-VAR:
試験成績書(COA)
製品のロット番号・バッチ番号を入力して、試験成績書(COA) を検索できます。ロット番号・バッチ番号は、製品ラベルに「Lot」または「Batch」に続いて記載されています。
Transcription factor E3 protects against cadmium-induced apoptosis by maintaining the lysosomal-mitochondrial axis but not autophagic flux in Neuro-2a cells
Pi H, et al.
Toxicology Letters, 295(4), 335-350 (2018)
Yun-Pei Zhang et al.
American journal of physiology. Gastrointestinal and liver physiology, 311(6), G1091-G1104 (2016-10-30)
LPS-induced microvascular hyperpermeability and hemorrhage play a key role in the development of sepsis, the attenuation of which might be an important strategy to prevent sepsis. However, the current clinical therapies have proven to be inefficient in improving the prognosis
Man Kyu Shim et al.
Journal of controlled release : official journal of the Controlled Release Society, 294, 376-389 (2018-12-15)
Cancer nanomedicine using nanoparticle-based delivery systems has shown outstanding promise in recent decades for improving anticancer treatment. However, limited targeting efficiency, low drug loading efficiency and innate toxicity of nanoparticles have caused severe problems, leaving only a few available in
Michael J Mitchell et al.
Nature communications, 8, 14179-14179 (2017-03-21)
Physical forces affect tumour growth, progression and metastasis. Here, we develop polymeric mechanical amplifiers that exploit in vitro and in vivo physical forces to increase immune cytokine-mediated tumour cell apoptosis. Mechanical amplifiers, consisting of biodegradable polymeric particles tethered to the
Katherine A Staines et al.
Journal of cellular physiology, 231(6), 1392-1404 (2015-12-08)
The transmembrane glycoprotein E11 is considered critical in early osteoblast-osteocyte transitions (osteocytogenesis), however its function and regulatory mechanisms are still unknown. Using the late osteoblast MLO-A5 cell line we reveal increased E11 protein/mRNA expression (P < 0.001) concomitant with extensive osteocyte dendrite
ライフサイエンス、有機合成、材料科学、クロマトグラフィー、分析など、あらゆる分野の研究に経験のあるメンバーがおります。.
製品に関するお問い合わせはこちら(テクニカルサービス)