すべての画像(1)
About This Item
実験式(ヒル表記法):
C4H10N2O2 · HCl
CAS番号:
分子量:
154.60
MDL番号:
UNSPSCコード:
12352209
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.32
おすすめの製品
アッセイ
≥97% (NMR)
フォーム
powder
光学活性
[α]/D +21 to +31°, c = 0.5 M in 0.1 M HCl(lit.)
保管条件
desiccated
色
white to beige
溶解性
H2O: soluble (solutions may be stored for several days at 4 °C)
保管温度
−20°C
SMILES記法
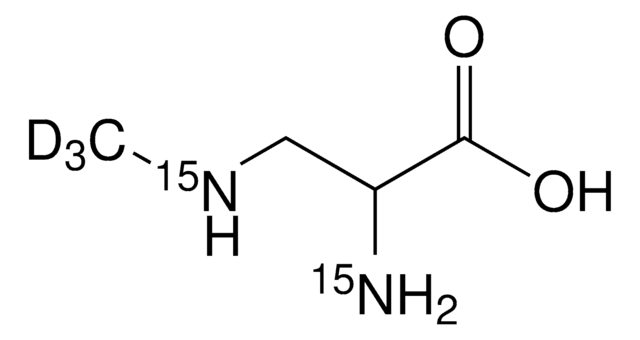
Cl.CNC[C@H](N)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C4H10N2O2.ClH/c1-6-2-3(5)4(7)8;/h3,6H,2,5H2,1H3,(H,7,8);1H/t3-;/m0./s1
InChI Key
VDXYGASOGLSIDM-DFWYDOINSA-N
詳細
L-BMAA塩酸塩/β-N-メチルアミノ-l-アラニン(BMAA)は、シアノバクテリア(藍藻)の神経毒です。
アプリケーション
L-BMAA塩酸塩は、砂漠殻物質中のβ-N-メチルアミノ-l-アラニン(BMAA)異性体の分析においてすべてのサンプルを比較するための標準物質として使用されています。また、Phaeodactylum tricornutum(羽状目海洋性珪藻)およびThalassiosira weissflogii(珪藻の一種)の細胞を処理してそれらに与える影響を研究するために、f/2+Si培地への添加剤としても使用されています。
生物化学的/生理学的作用
L-BMAA塩酸塩は、グリピカン-1へのヘパラン硫酸塩の添加を抑えるのに役立ちます。異常なグルタミン酸受容体結合特性を有します。筋萎縮性側索硬化症/Lou Gehrig病を引き起こす場合があります。′
保管分類コード
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
引火点(°F)
Not applicable
引火点(℃)
Not applicable
個人用保護具 (PPE)
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
適用法令
試験研究用途を考慮した関連法令を主に挙げております。化学物質以外については、一部の情報のみ提供しています。 製品を安全かつ合法的に使用することは、使用者の義務です。最新情報により修正される場合があります。WEBの反映には時間を要することがあるため、適宜SDSをご参照ください。
Jan Code
B107-VAR:
B107-50MG:
B107-10MG:
B107-BULK:
Neurotoxic amino acids and their isomers in desert environments
Metcalf JS, et al.
Journal of arid environments, 140-144 (2015)
David A Davis et al.
Journal of neuropathology and experimental neurology, 79(4), 393-406 (2020-02-23)
The early neuropathological features of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/motor neuron disease (ALS/MND) are protein aggregates in motor neurons and microglial activation. Similar pathology characterizes Guamanian ALS/Parkinsonism dementia complex, which may be triggered by the cyanotoxin β-N-methylamino-l-alanine (BMAA). We report here the
Olga A Koksharova et al.
Toxins, 12(6) (2020-06-10)
All cyanobacteria produce a neurotoxic non-protein amino acid β-N-methylamino-L-alanine (BMAA). However, the biological function of BMAA in the regulation of cyanobacteria metabolism still remains undetermined. It is known that BMAA suppresses the formation of heterocysts in diazotrophic cyanobacteria under nitrogen
2-Amino-β-methylamino-propionc acid, a new amino acid from seeds of Cycas circinali.
Vega, et al.
Psychochemistry, 6, 759-762 (1967)
Johan Eriksson et al.
Amino acids, 36(1), 43-48 (2008-01-12)
Two different assays have been developed and used in order to investigate the optimal conditions for derivatization and detection of acid beta-N-methyl-amino-L-alanine (BMAA) in a cyanobacterial sample. BMAA was extracted from cyanobacterial cultures both from the cytosolic ("free") fraction and
ライフサイエンス、有機合成、材料科学、クロマトグラフィー、分析など、あらゆる分野の研究に経験のあるメンバーがおります。.
製品に関するお問い合わせはこちら(テクニカルサービス)