32830
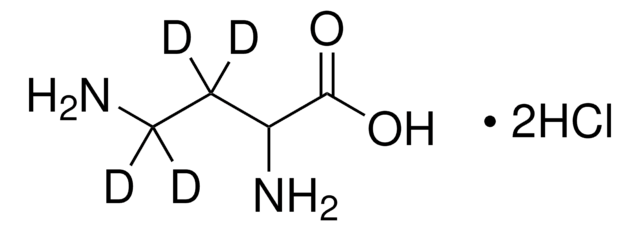
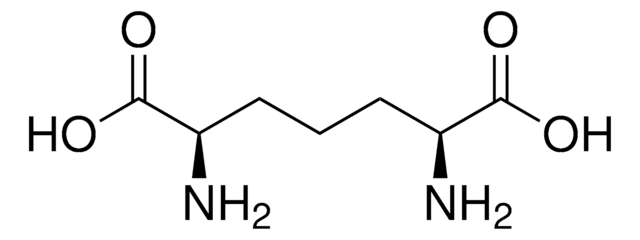
L-2,4-Diaminobutyric acid dihydrochloride
≥95.0%
別名:
(2S)-2,4-Diaminobutanoic acid dihydrochloride, L-2,4-Diaminobutanoic acid dihydrochloride
About This Item
おすすめの製品
品質水準
アッセイ
≥95.0% (AT)
≥95.0%
光学活性
[α]20/D +14.5±1.5°, c = 3.67% in H2O
反応適合性
reaction type: solution phase peptide synthesis
mp
197-200 °C (dec.)
溶解性
water: soluble 0.5 g/10 mL
アプリケーション
peptide synthesis
SMILES記法
Cl.Cl.NCC[C@H](N)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C4H10N2O2.2ClH/c5-2-1-3(6)4(7)8;;/h3H,1-2,5-6H2,(H,7,8);2*1H/t3-;;/m0../s1
InChI Key
CKAAWCHIBBNLOJ-QTNFYWBSSA-N
類似した製品をお探しですか? 訪問 製品比較ガイド
関連するカテゴリー
詳細
アプリケーション
注意
シグナルワード
Danger
危険有害性情報
危険有害性の分類
Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
ターゲットの組織
Respiratory system
保管分類コード
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
引火点(°F)
Not applicable
引火点(℃)
Not applicable
個人用保護具 (PPE)
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
適用法令
試験研究用途を考慮した関連法令を主に挙げております。化学物質以外については、一部の情報のみ提供しています。 製品を安全かつ合法的に使用することは、使用者の義務です。最新情報により修正される場合があります。WEBの反映には時間を要することがあるため、適宜SDSをご参照ください。
Jan Code
32830-25G:
32830-BULK:
32830-5G:
32830-1G:
32830-VAR:
最新バージョンのいずれかを選択してください:
ライフサイエンス、有機合成、材料科学、クロマトグラフィー、分析など、あらゆる分野の研究に経験のあるメンバーがおります。.
製品に関するお問い合わせはこちら(テクニカルサービス)