おすすめの製品
アッセイ
≥98% (HPLC)
フォーム
powder
テクニック
HPLC: suitable
色
white
mp
160 °C
溶解性
water: 50 mg/mL, clear, colorless
保管温度
2-8°C
SMILES記法
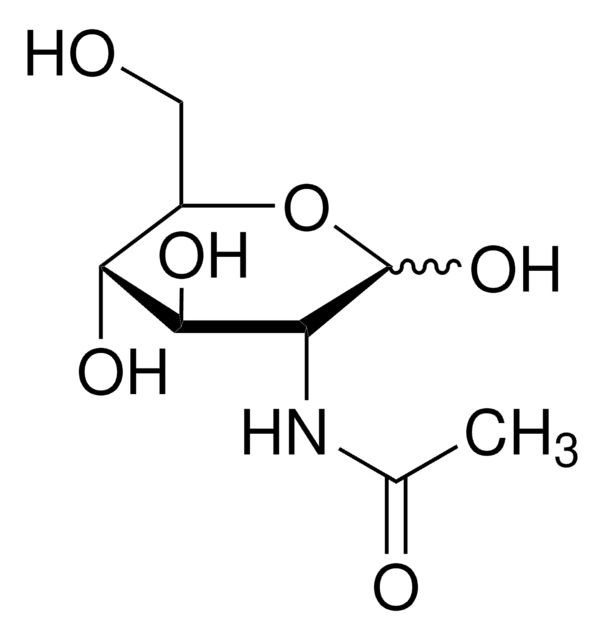
CC(=O)N[C@H]1C(O)O[C@H](CO)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O
InChI
1S/C8H15NO6/c1-3(11)9-5-7(13)6(12)4(2-10)15-8(5)14/h4-8,10,12-14H,2H2,1H3,(H,9,11)/t4-,5-,6+,7-,8?/m1/s1
InChI Key
OVRNDRQMDRJTHS-KEWYIRBNSA-N
類似した製品をお探しですか? 訪問 製品比較ガイド
詳細
アミノ糖であるN-アセチル-D-ガラクトサミン(GalNAc)は、多くの O結合型グリカン構造とN結合型グリカン構造の成分です。ウリジン二リン酸(UDP)-GalNAcであるGalNAcは、タンパク質グリコシル化において多くのセリン残基およびスレオニン残基に対する最初のO結合型糖です。
アプリケーション
N-アセチル-D-ガラクトサミンは、次のように使用されています:
- レクチンビーズ結合アッセイにおけるDolichos biflorus (ヒマラヤフジマメ)凝集素(DBA)ハプテン糖として
- レクチンブロット阻害を用いるレクチン結合の特異性の評価
- 免疫組織化学的検査においてWisteria floribunda 由来レクチンを事前吸着させるため
アミノ糖であるN-アセチル-D-ガラクトサミン(GalNAc)は、多くのO結合およびN結合グリカン構造の成分です。 UDP-GalNAcの形を取るGalNAcは、タンパク質グリコシル化において多くのセリン残基およびスレオニン残基になる初期O結合糖です。
保管分類コード
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
引火点(°F)
Not applicable
引火点(℃)
Not applicable
個人用保護具 (PPE)
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
適用法令
試験研究用途を考慮した関連法令を主に挙げております。化学物質以外については、一部の情報のみ提供しています。 製品を安全かつ合法的に使用することは、使用者の義務です。最新情報により修正される場合があります。WEBの反映には時間を要することがあるため、適宜SDSをご参照ください。
Jan Code
A2795-100MG:
A2795-BULK:
A2795-5G:
A2795-1G:
A2795-500MG:
A2795-VAR:
A2795-RSAMPLE:
A2795-10MG:
A2795-25G:
この製品を見ている人はこちらもチェック
P Van den Steen et al.
Critical reviews in biochemistry and molecular biology, 33(3), 151-208 (1998-07-23)
The biosynthesis, structures, and functions of O-glycosylation, as a complex posttranslational event, is reviewed and compared for the various types of O-glycans. Mucin-type O-glycosylation is initiated by tissue-specific addition of a GalNAc-residue to a serine or a threonine of the
Sian F Irvine et al.
International journal of molecular sciences, 19(4) (2018-04-13)
Perineuronal nets (PNNs) are extracellular matrix structures surrounding neuronal sub-populations throughout the central nervous system, regulating plasticity. Enzymatically removing PNNs successfully enhances plasticity and thus functional recovery, particularly in spinal cord injury models. While PNNs within various brain regions are
Yuki Kuramoto et al.
Journal of molecular and cellular cardiology, 121, 256-265 (2018-07-27)
Fabry disease is an X-linked disease caused by mutations in α-galactosidase A (GLA); these mutations result in the accumulation of its substrates, mainly globotriaosylceramide (Gb3). The accumulation of glycosphingolipids induces pathogenic changes in various organs, including the heart, and Fabry
Malte Lenders et al.
Nephrology, dialysis, transplantation : official publication of the European Dialysis and Transplant Association - European Renal Association, 32(12), 2090-2097 (2016-09-30)
Renal and cardiac involvement is responsible for substantial morbidity and mortality in Fabry disease (FD). We analysed the incidence of FD-related renal, cardiac and neurologic end points in patients with FD on long-term enzyme replacement therapy (ERT). A retrospective analysis
David J Gill et al.
Trends in cell biology, 21(3), 149-158 (2010-12-15)
O-GalNAc glycosylation of proteins confers essential structural, protective and signaling roles in eumetazoans. Addition of O-glycans onto proteins is an extremely complex process that regulates both sites of attachment and the types of oligosaccharides added. Twenty distinct polypeptide GalNAc-transferases (GalNAc-Ts)
ライフサイエンス、有機合成、材料科学、クロマトグラフィー、分析など、あらゆる分野の研究に経験のあるメンバーがおります。.
製品に関するお問い合わせはこちら(テクニカルサービス)